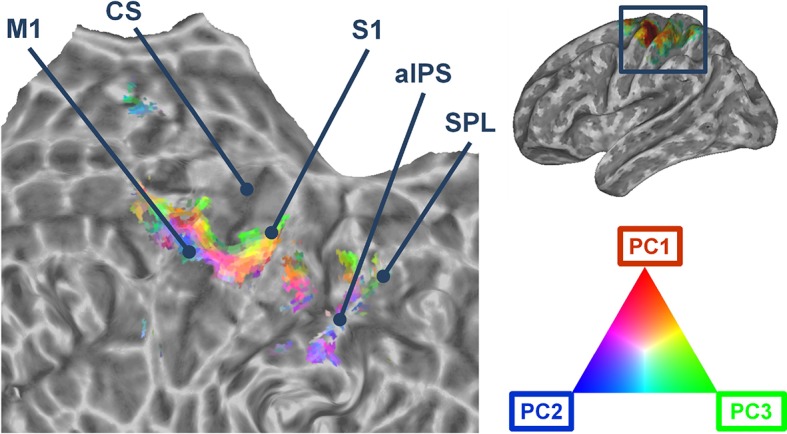
Figure 2. Cortical flattened map depicting the topographical organization of the first three synergies across primary motor, somatosensory, and parietal regions.
The portion of cerebral cortex represented in the map corresponds to the area enclosed in the rectangle in the brain mesh (top, right). M1: Primary Motor Cortex. CS: Central Sulcus. S1: Primary Somatosensory cortex (postcentral gyrus). aIPS: anterior intraparietal sulcus. SPL: Superior Parietal lobule.