Extended Data Figure 7.
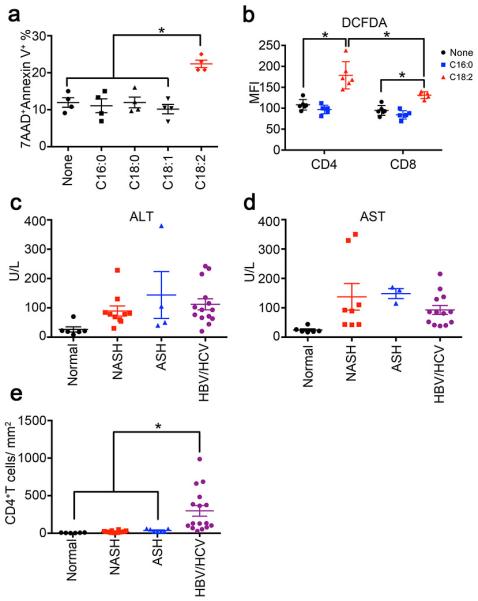
Linoleic acid induces cell death in human CD4+ T lymphocytes, and NASH patients have lower intrahepatic CD4+ T lymphocytes.
a, Cell death levels of sorted human CD4+ T lymphocytes treated with different free fatty acids. Mean ± SEM; n=4 *p<0.05, one-way ANOVA. b, ROS level of CD4+ or CD8+ T lymphocyte in PBMC treated with linoleic acid or palmitic acid. Mean ± SEM; n=6 *p<0.05, two-way ANOVA. c,d, serum ALT and AST concentration in different patients. e, Intrahepatic CD4+ T lymphocyte count in biopsies. CD4+ T lymphocytes were identified by immunohistochemistry. Mean ± SEM; normal=6, NASH=16, ASH=8, HBV/HCV=16, *p<0.05, one-way ANOVA.
