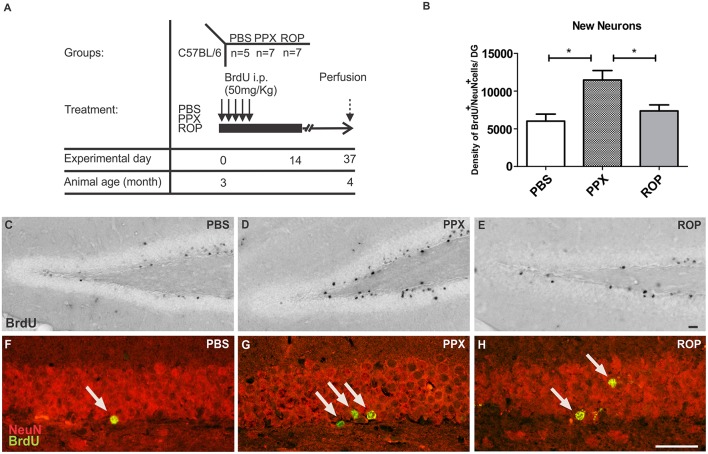
Figure 3.
PPX only increases the generation of new neurons in the murine DG. (A) Survival paradigm. At the beginning, 3-month-old animals received PPX, ROP or PBS i.p. for 14 days. During the first 5 days, all mice were i.p. injected with BrdU (50 mg/kg). Animals were perfused 32 days after the last BrdU injection. (B) Hippocampal neurogenesis (calculated density of BrdU+/NeuN+ neurons) was increased after PPX compared to PBS. No change in DG neurogenesis was observed after ROP treatment. Representative stainings of BrdU+ in the DG of the hippocampus of PBS (C), PPX (D), and ROP (E) treated mice show a significant increase in PPX-injected animals compared to ROP- and PBS-injected controls. Confocal microscopy depicts double-labeled BrdU+ (green)/NeuN+ (red) neurons in the hippocampal DG of PBS (F), PPX (G), and ROP-injected mice (H). Error bars represent mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-hoc test, *p < 0.05. Scale bars: 20 μm (C–H).