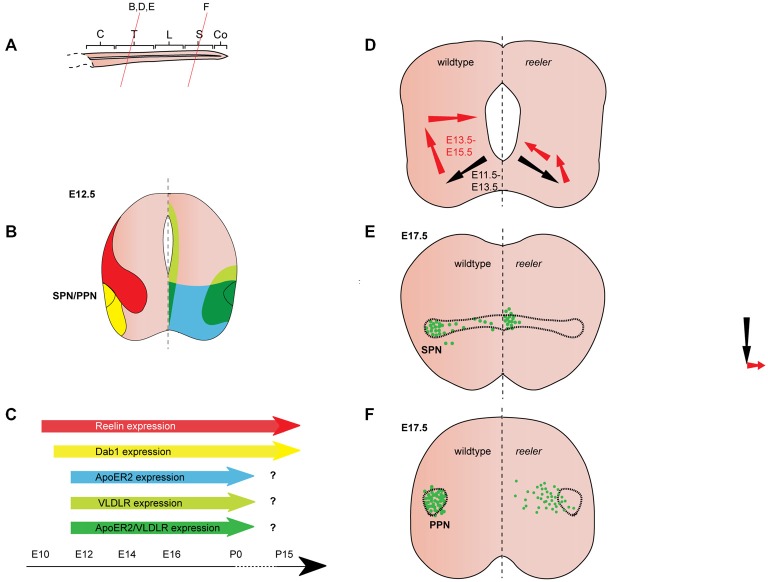
Figure 3.
Reelin signaling in the migration of autonomic preganglionic neurons. (A) Sagittal view of embryonic spinal cord (C, cervical; T, thoracic; L, lumbar; S, sacral; Co, coccygeal). Red lines indicate level of coronal section in (D–F). (B) Expression patterns of Reelin (red), Dab1 (yellow), ApoER2 (green) and VLDLR (green) at the indicated time point. Reelin and Dab1 expression are only presented in the left half of the brain; ApoER2 and VLDLR expression are only presented in the right half of the brain. (C) Expression of Reelin, Dab1, ApoER2 and VLDLR over time. (D) Schematic of migratory paths of preganglionic autonomic neurons in wildtype mice (left half of the brain) and reeler mutants (right half of the brain). Black arrows indicate radial migration; red arrows indicate tangential migration. Radial migration is unaffected in reeler mutants, but in the second step of migration the majority of preganglionic autonomic neurons migrate to an ectopic position in the medial regions of the spinal cord. (E) SPN distribution at E17.5 in wildtype (left half of the brain) and reeler (right half of the brain) mice. Sympathetic preganglionic neurons (SPNs) are ectopically located close to the central canal in reeler mice. (F) Parasympathetic preganglionic neuron (PPN) distribution at E17.5 in wildtype mice (left half of the brain) and reeler mutants (right half of the brain). PPN are disorganized and distributed along the mediolateral axis of the intermediate spinal cord in reeler mutants.