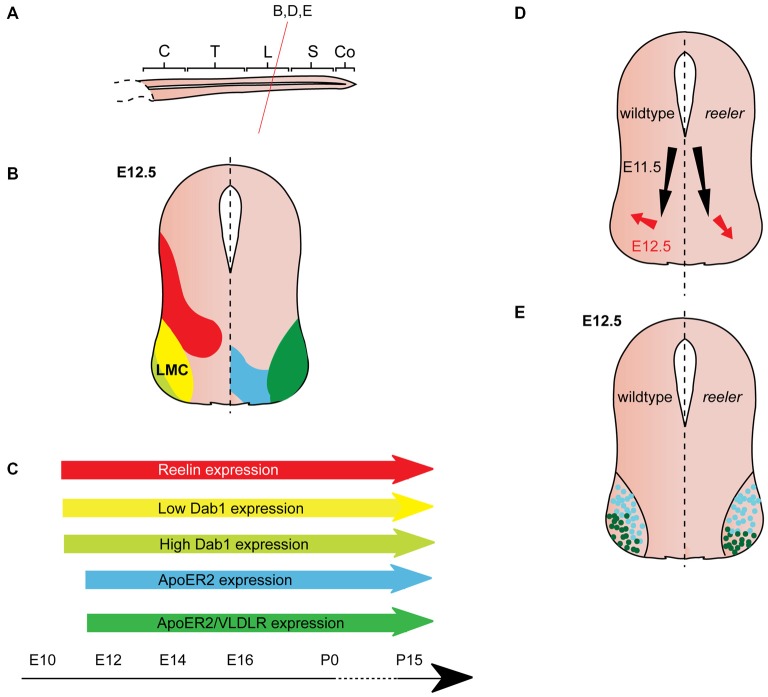
Figure 4.
Reelin signaling in motor neuron migration. (A) Sagittal view of embryonic spinal cord (C, cervical; T, thoracic; L, lumbar; S, sacral; Co, coccygeal). Red line indicates level of coronal section in (D,E). (B) Expression patterns of Reelin (red), Dab1 (low levels: yellow, high levels: light green), ApoER2 (blue) and ApoER2/VLDLR (green) at the indicated time point. Low-level Dab 1 expression is restricted to Foxp1+, Isl1+ neurons in the medial part of the lateral motor column (LMC), high-level Dab1 expression is found in Foxp1+, Lhx1+ neurons in the lateral LMC. Reelin and Dab1 expression are only presented in the left half of the brain; ApoER2 and VLDLR expression are only presented in the right half of the brain. (C) Expression of Reelin, Dab1, ApoER2 and VLDLR over time. (D) Schematic of migratory paths of somatic motor neurons (SMNs) in wildtype mice (left half of the brain) and reeler mutants (right half of the brain). Black arrows indicate ventral radial migration of SMNs from the neuroepithelium to the LMC; red arrows indicate a short tangential migratory step, which enables a subset of SMNs to migrate dorsolaterally to form the lateral LMC. Radial migration is unaffected in reeler mice, but the dorsolateral migration is altered. (E). As compared to their wildtype counterparts, lateral LMC neurons (Foxp1+, Lhx1+; dark green dots) settle in more ventromedial positions in the reeler spinal cord. Turquoise dots represent medial LMC neurons (Foxp1+, Isl1+).