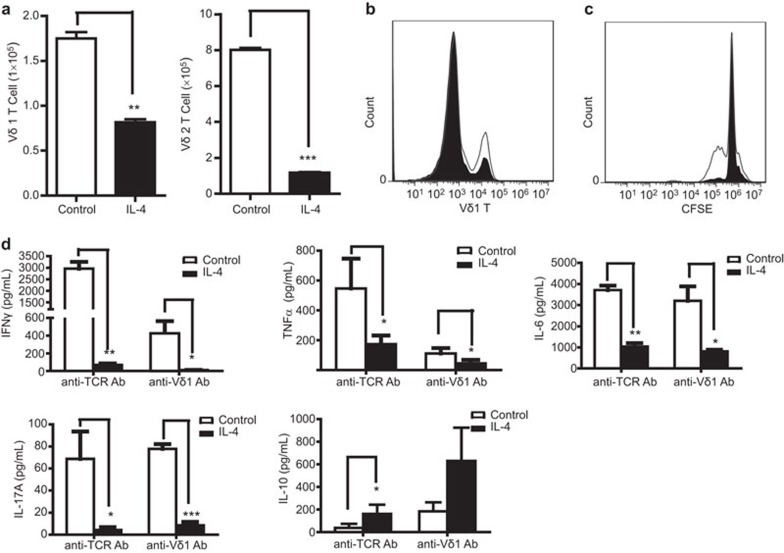
Figure 1.
IL-4 inhibits the activation of both Vδ1 and Vδ2 T cells in vitro. Vδ1T cells or Vδ2 T cells in fresh PBMCs were activated by immobilized anti-TCR Vδ1 mAb or zoledronic acid and cultured in RPMI 1640 medium with 100 IU IL-2 in the presence or absence of IL-4 (5 ng/ml). (a) The absolute numbers of Vδ1 T cells (left) or Vδ2 T cells (right) after 5 days were analyzed by flow cytometry. One representative experiment of three independent experiments is shown. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. (b) The relative ratio of Vδ1 T cells with (shaded histogram) and without (open histogram) IL-4 treatment (5 ng/ml) was analyzed by flow cytometry. One representative of three independent experiments is shown. (c) The fresh PBMCs were labeled with CFSE and expanded by anti-Vδ1 mAb. The data demonstrate the proliferation of Vδ1 T cells with (shaded histogram) and without (open histogram) IL-4 treatment at 5.5 days. One representative of three independent experiments is shown. (d) γδ T cells were activated by anti-human TCR PAN γδ mAb or anti-human Vδ1 mAb and cultured for 7 days. The cytokines IFNγ, TNFα, IL-6, IL-17A and IL-10 in the culture supernatant were assayed by ELISA or the Milliplex method. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD Accuri C6 flow cytometer system. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. IFN, interferon; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; TCR, T-cell receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.