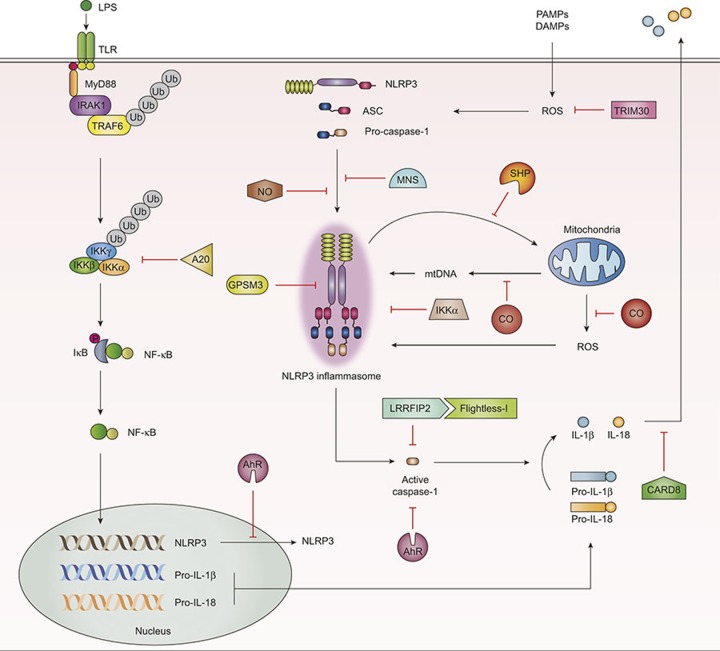
Figure 3.
Schematic models for the identified negative regulators in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. A20, a well-known inhibitor for NF-κB signaling, acts as a negative regulator of NLRP3 activation and caspase-1 processing. AhR binds to the xenobiotic response element in the NLRP3 promoter and inhibits NLRP3 transcription. Several molecules (e.g., NO, MNS, GPSM3, CARD8, IKKα) play a critical role in the modulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly. NO and MNS inhibit formation of the ASC pyroptosome and speck formation by targeting the NLRP3 complex. GPSM3 and CARD8 directly bind to NLRP3 and act as negative regulators of the NLRP3 inflammasome. IKKα negatively controls the NLRP3 inflammasome through interaction with the ASC adaptor molecule. LRRFIP2 interacts with Flightless-1, a pseudosubstrate of caspase-1, and inhibits caspase-1 activation. The orphan nuclear receptor SHP interacts with NLRP3, and mediates translocation of NLRP3 into mitochondria, thus regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. CO plays a general inhibitory role in mitochondrial ROS generation and translocation of mitochondrial DNA into cytosol. TRIM30 also inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome activation through modulation of ROS generation, although there is no evidence that it can bind to any partner in NLRP3 inflammasome assembly. ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a C-terminal caspase recruitment domain; A20, tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; CARD8, caspase recruitment domain; CO, carbon monoxide; IKKα, IκB kinase α GPSM3, G protein signaling modulator-3; LRRFIP2, leucine-rich repeat Fli-I-interacting protein 2; MNS, 3,4-methylenedioxy-β-nitrostyrene; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NLRP3, NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 3; NO, nitric oxide; SHP, small heterodimer partner; TRIM30, tripartite-motif protein 30.