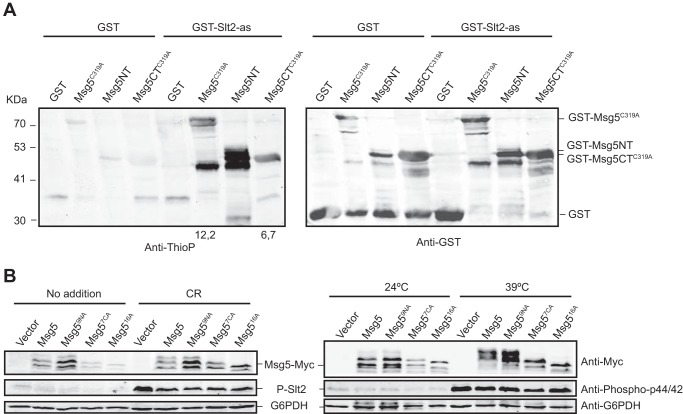
FIGURE 4.
GST-Slt2-as thiophosphorylates recombinant GST-Msg5 in both the N- and C-terminal domains. A, Western blot analysis of the kinase assay performed as in Fig. 3B but using as substrate E. coli extracts expressing the catalytically inactive version GST-Msg5C319A from plasmid pGEX-KG-msg5C319A or the two halves of this protein GST-Msg5NT (residues 1–227) and GST-Msg5CTC319A (residues 228–489) from plasmids pGEX-KG-msg5NT and pGEX-KG-msg5CTC319A, respectively. Anti-thiophosphate (Anti-ThioP) ester antibodies (left panel) and anti-GST (right panel) were used to detect thiophosphorylated proteins and GST or GST-Msg5, respectively. Numbers below the blot indicate the amount of thiophosphorylated GST-Msg5C319A and GST-Msg5TC319A in the kinase assay using GST-Slt2-as normalized with respect to their amount in the control kinase assay with GST. Due to signal saturation, the relative amount of thiophosphorylated GST-Msg5NT is not indicated. B, Western blot analysis of extracts from the mutant strain DD1–2D (msg5Δ) transformed with YCplac22 (vector), YCplac22-MSG5m, YCplac22-msg5N9Am, YCplac22-msg5C7Am, or YCplac22-msg516Am, growing at 24 °C under the absence (No addition) or presence of Congo red (30 μg/ml) for 3 h (left panels) or at 39 °C for 1 h (right panels) as indicated. Phosphorylated Slt2, Myc-tagged proteins, and G6PDH (as loading control) were detected with anti-phospho-p44/42, anti-Myc, and anti-G6PDH antibodies, respectively.