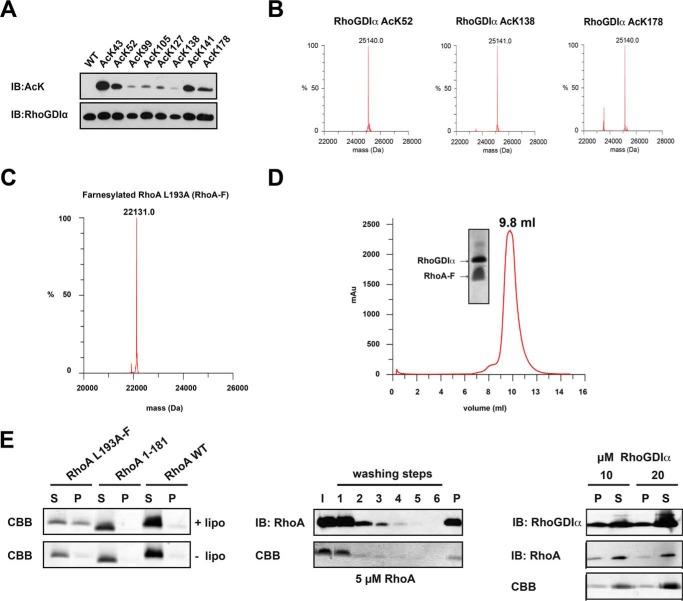
FIGURE 3.
Farnesylated RhoA is functional in binding to RhoGDIα, liposome binding, and extraction by RhoGDIα. A, RhoGDIα is lysine-acetylated using the genetic code expansion concept. The acetyl-l-lysine incorporation was verified by anti-acetyl-l-lysine IB. B, quantitative incorporation of N-(ϵ)-acetyl-l-lysine into RhoGDIα, as judged by ESI-mass spectrometry. The molecular masses correspond exactly (±1 Da) to the protein mass calculated (His6-RhoGDIα, 25,099.1 Da; single-acetylated RhoGDIα, 25,099.1 ± 42 Da; double-acetylated RhoGDIα, 25,099.1 ± 84 Da). C, RhoA is homogeneously and quantitatively farnesylated, as judged by ESI-mass spectrometry (expected mass, 22,131.2 Da). D, analytical size exclusion chromatography of a RhoA-F·RhoGDIα complex (Superdex 75 10/300). RhoA-F binds tightly to RhoGDIα coeluting from the gel filtration column at an elution volume of 9.8 ml. Notably, RhoA-F alone elutes at 11.9 ml (data not shown). E, RhoA-F liposome binding and extraction by RhoGDIα. Left, RhoA binds to liposomes, dependent on the presence of the farnesyl moiety, as shown by a liposome cosedimentation assay. To this end, liposomes were prepared and incubated with RhoA-F, C-terminally deleted RhoA 1–181, and full-length but non-prenylated RhoA. After ultracentrifugation, only the farnesylated full-length RhoA-F was detectable in the pellet fraction and cosedimented with the liposomes, whereas the other RhoA proteins can only be detected in the soluble fraction, as shown by SDS-PAGE and staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB). Middle, liposomes can be loaded with farnesylated RhoA-F. After loading of liposomes with farnesylated RhoA-F, non-bound RhoA-F can be removed from the supernatant by consecutive washing. After six washing steps, no RhoA-F can be detected in the supernatant, neither by immunoblotting using a specific anti-RhoA antibody nor by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. RhoA-F can be detected only in the pellet fraction after cosedimentation of the liposomes, showing that the liposomes are loaded with RhoA-F. Right, RhoGDIα can solubilize RhoA-F from RhoA-F-loaded liposomes in a concentration-dependent manner. RhoA-F-charged liposomes were treated with increasing concentrations of RhoGDIα, as indicated. With 20 μm RhoGDIα, there is more RhoA-F solubilized from the liposomes compared with the sample with 10 μm RhoGDIα. RhoGDIα is stained by immunoblotting using an anti-RhoGDIα antibody, and RhoA is stained by an anti-RhoA antibody. I, input; S, supernatant; P, pellet.