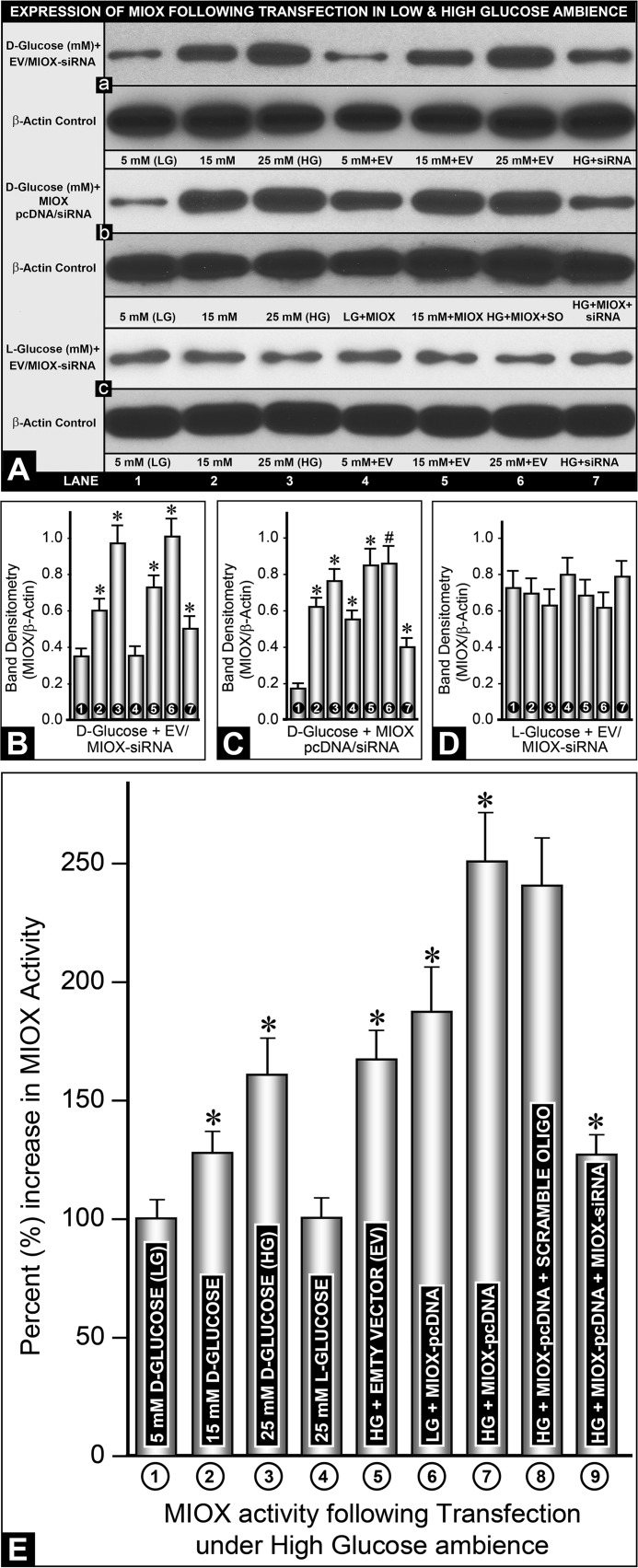
FIGURE 3.
Expression and activity of MIOX in LLC-PK1 cells following its overexpression in HG ambience. Western blotting analyses show a dose-dependent increased expression of MIOX in response to various d-glucose concentrations, whereas treatment with MIOX-specific siRNA caused a marked reduction in its expression (A (a) and B). Transfection with MIOX-pcDNA increased the expression of MIOX at LG and HG, which was normalized to basal levels with MIOX siRNA treatment (A (b) and C). Exposure of l-glucose induced no significant change in the expression of MIOX at its high or low concentrations and with or without pcDNA transfection or siRNA treatment (A (c) and D). The expression of β-actin, serving as control, was unchanged. E, MIOX activity; at basal levels (LG), it was designated as 100%, and a relative percentage increase in various samples was calculated. A dose-dependent increase in enzyme activity was observed with various concentrations of d-glucose but not with l-glucose or transfection of EV (E, columns 1–5). However, MIOX-pcDNA transfection led to a ∼2-fold increase in enzyme activity even at LG concentration, whereas it increased by another 50% under HG ambience, and it was normalized to almost basal levels with MIOX siRNA treatment (E, columns 6, 7, and 9). Scramble oligonucleotide had no significant effect on HG-induced MIOX activity in MIOX-pcDNA-transfected cells (E, column 8). Band densities normalized to the respective β-actin band densities of various blots of each variable (A (a–c)), compared with their respective controls, are shown in bar graphs in B–D (n = 4; *, p < 0.01; #, p < 0.05). Error bars, S.D.