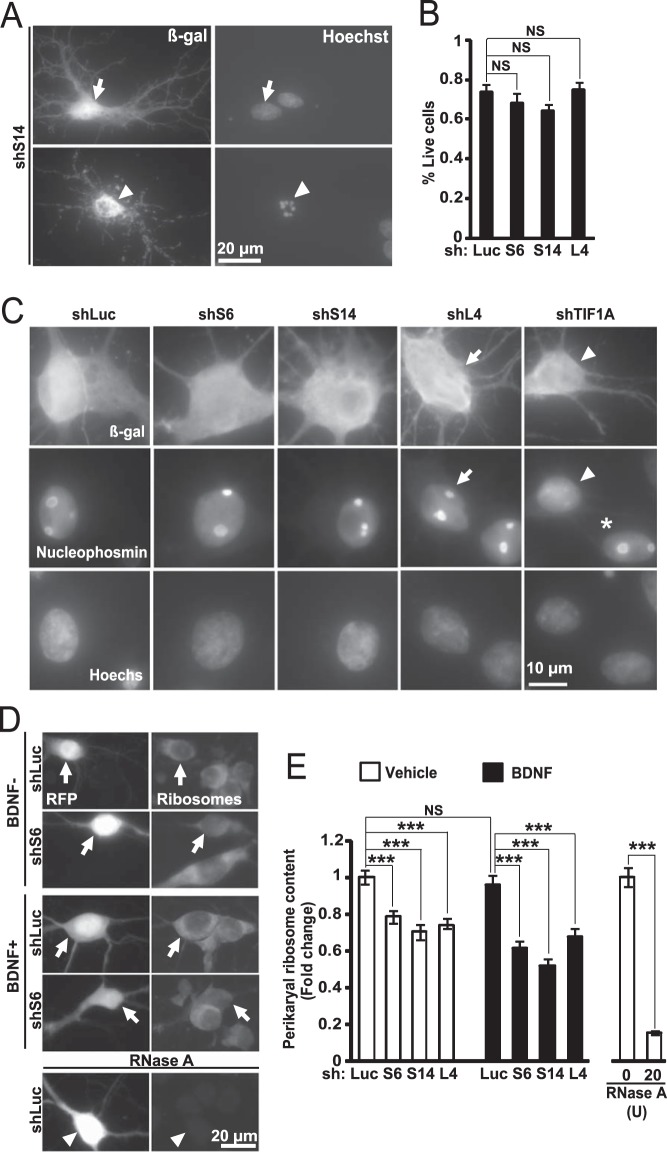
FIGURE 5.
In hippocampal neurons, inhibition of ribosomal biogenesis results in ribosome depletion without cell death or nucleolar disruption. DIV6 hippocampal neurons were co-transfected with shRNAs against RPs together with an expression vector for β-gal (A and B) or EGFP (C) or RFP (D and E) (0.4 + 0.2 μg of plasmid DNAs/2·105 neurons, respectively). Neuronal survival, nucleolar integrity, and perikaryal ribosome content were evaluated 3 days later. A and B, knockdowns of ribosomal proteins did not affect neuronal viability. Transfected cells were identified by β-gal immunostaining; nuclear morphology was visualized witch Hoechst-33258. A, transfected neurons with non-condensed nuclei were counted as live cells (arrows); presence of condensed and/or fragmented chromatin identified dead cells (arrowhead). B, quantitation of surviving fraction of transfected neurons. Data represent means ± S.E. of three independent experiments; NS, not significant; p > 0.05, U test. C, integrity of neuronal nucleoli after ribosomal protein knockdowns. Neuronal integrity was determined using nucleophosmin immunostaining; nuclei were counter-stained with Hoechst-33258. In neurons that received control shRNA (shLuc) or shRPs, the nucleophosmin signal was concentrated in the nucleoli (arrows). Conversely, when pol 1 activity was disrupted with shTIF1A, most nucleophosmin was nucleoplasmic (arrowhead); an adjacent untransfected neuron displayed nucleolar nucleophosmin (asterisk). D and E, reduced somatic ribosome content after inhibition of ribosomal biogenesis. On DIV7, 10 ng/ml BDNF was added to some cultures as indicated. D, representative images of ribosome staining in transfected neurons (e.g. RFP-positive; arrows). Note that pre-treatment with RNaseA abolished the ribosome signal (arrowhead). E, quantification of the perikaryal ribosome content. Data represent means ± S.E. of at least 45 individual cells from three independent experiments; two-way ANOVA, effect of shRNA, F3,556 = 39.543, p < 0.001; post hoc tests: ***, p < 0.001; NS, p > 0.05.