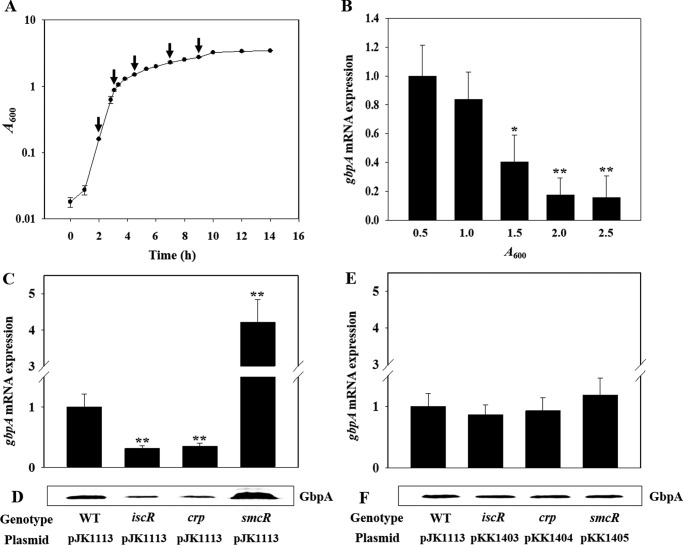
FIGURE 3.
Effects of growth phases and global regulatory proteins on the gbpA expression. Upper panel, growth kinetics of V. vulnificus and growth phase-dependent expression of gbpA. A, growth of the wild type culture in LBS was monitored spectrophotometrically at 600 nm (A600), and total RNAs were isolated from the cells harvested at different growth phases (from left, at A600 of 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, and 2.5) as indicated by arrows. B, gbpA mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR analyses, and the gbpA mRNA level in the cells grown to an A600 of 0.5 was set as 1. Error bars represent the S.D. *, p < 0.05, and **, p < 0.005 relative to the cells grown to an A600 of 0.5. Lower panel, expression of gbpA in V. vulnificus with different genetic backgrounds. Samples were harvested from the cultures of the wild type (WT) and isogenic mutants grown aerobically to an A600 of 0.5 and analyzed to determine the gbpA mRNA and GbpA protein levels. C and E, gbpA mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR analyses, and the gbpA mRNA level in the wild type was set as 1. **, p < 0.005 relative to the wild type. D and F, protein samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and GbpA was detected by Western blotting using the rabbit anti-V. vulnificus GbpA serum. (pJK1113), wild type; iscR (pJK1113), iscR mutant; smcR (pJK1113), smcR mutant; crp (pJK1113), crp mutant; iscR (pKK1403), crp (pKK1404), and smcR (pKK1405), complemented strains.