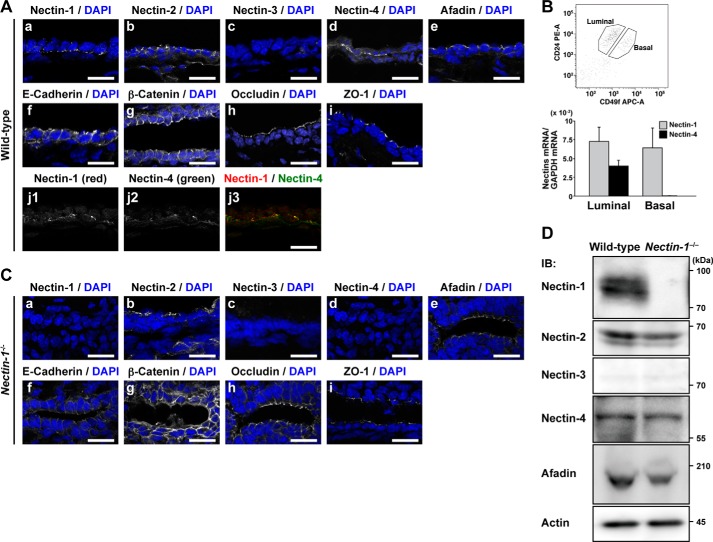
FIGURE 2.
Localization of nectin-1 and nectin-4 at the boundary between the luminal and basal cells. A, panels a–j, localization of cell adhesion components in the mammary epithelium of pregnancy day 18.5 wild-type mice. The sections were stained with the indicated Abs. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. A, panel j, co-localization of nectin-1 and nectin-4 at the boundary between the luminal and basal cells. Scale bars, 20 μm. B, nectin-1 and nectin-4 mRNA expression in the luminal and basal cells. RNAs extracted from the sorted luminal cells, a CD49fmedCD24+ population, and basal cells, a CD49fhighCD24+ population, were subjected to semiquantitative real time PCR. Error bars, S.E. C, panels a–i, localization of cell adhesion components in the mammary epithelium of pregnancy day 18.5 nectin-1−/− mice. The sections were stained with the indicated Abs. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Scale bars, 20 μm. D, expression levels of nectin-1, nectin-2, nectin-3, nectin-4, and afadin in the mammary epithelium of pregnancy day 18.5 wild-type and nectin-1−/− mice. The lysates (10 μg of protein each) of the mammary epithelium from pregnancy day 18.5 wild-type and nectin-1−/− mice were subjected to Western blotting using their respective Abs. Actin was used as a loading control. Results are representative of three independent experiments. PE, phycoerythrin; APC, allophycocyanin; IB, immunoblotting.