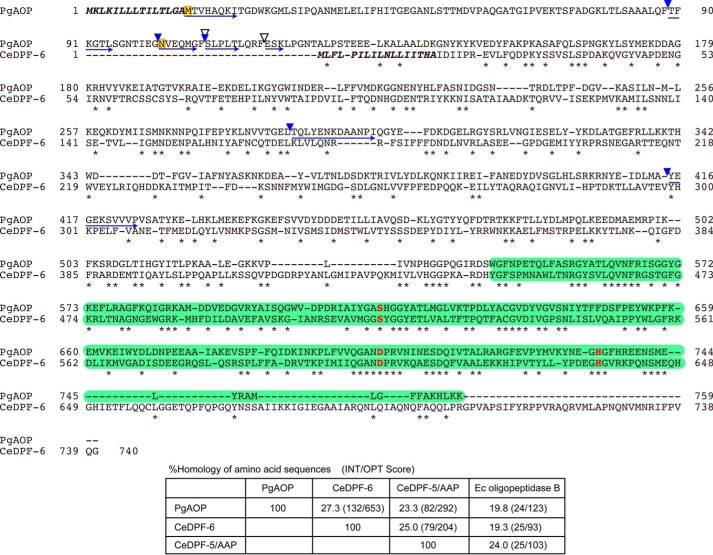
FIGURE 2.
Comparison of amino acid sequences between PGN_1349 and C. elegans DPF-6. The amino acid sequence of PGN_1349 (PgAOP) was compared with that of C. elegans DPF-6 (CeDPF-6). Identical amino acids are indicated by asterisks. Potential sets of 3 amino acids (Ser615, Asp702, and His734) forming the essential triad of serine peptidases are indicated by red boldface letters. Putative signal sequences are shown in boldface italic type, and peptidase S9 family domains (residues 544–759 on PgAOP and 445–662 on CeDPF-6) are shown by green boxes. The starting amino acids (Met16 and Asn102) of recombinant proteins expressed in this study (see Fig. 5) are boxed in yellow. N-terminal sequences and the autoproteolytic cleavage sites producing 75-kDa species in the purified sample and 75- and 52-kDa species appearing after incubation at 37 °C for 6 days (Fig. 5) are indicated by blue arrows and arrowheads, respectively. Chymotryptic cleavage sites are indicated by open arrowheads. Bottom, percent homology of amino acid sequences among PgAOP, CeDPF-6, CeDPF-5/AAP, and E. coli (Ec) oligopeptidase B were determined using Genetyx software.