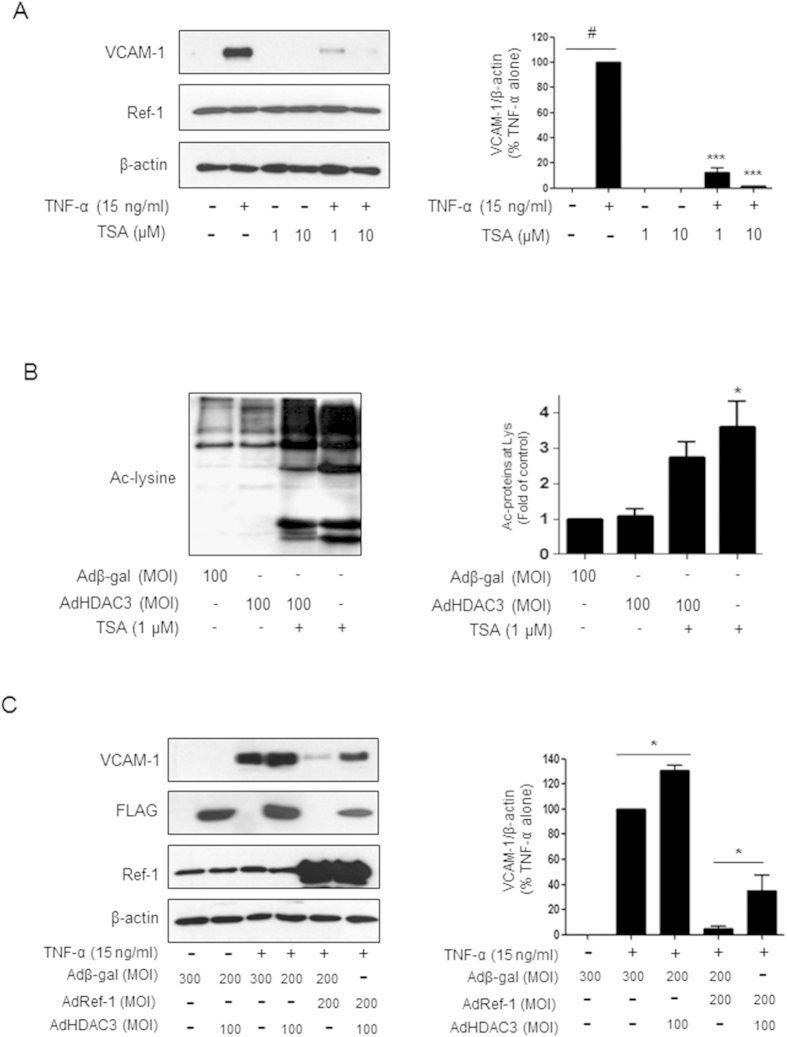
Figure 1. Trichostatin A (TSA) treatment caused downregulation of VCAM-1 expression in TNF-α-stimulated HUVECs.
(A) Effect of trichostatin A (TSA)-mediated acetylation on VCAM-1 expression in TNF-α-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Cells were treated with TSA (1, or 10 μM) in the presence or absence of TNF-α (15 ng/ml). (B) Acetylation and deacetylation profiles of intracellular proteins in response to 1 μM TSA treatment and histone deacetylase3 (HDAC3) expression, respectively. (C) Effects of APE1/Ref-1 or HDAC3 overexpression on VCAM-1 expression in TNF-α-stimulated HUVECs. Recombinant β-galactosidase adenovirus was used as a control. The blots were stripped and reprobed with anti-APE1/Ref-1 or β-actin antibodies to ensure protein loading. Representative blots are shown. Bar graph shows densitometry quantification of western blot data. The data are represented as % densitometry values of TNF-α-induced VCAM-1 expression. Columns, mean (n = 3); bars, SE. ***P < 0.001, significantly different from TNF-α-treated control cells; *P < 0.01 significantly different from cells expressing HDAC3; #P < 0.01 significantly different from untreated control cells based on a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Dunnett’s tests. Similar results were observed in replicate experiments.