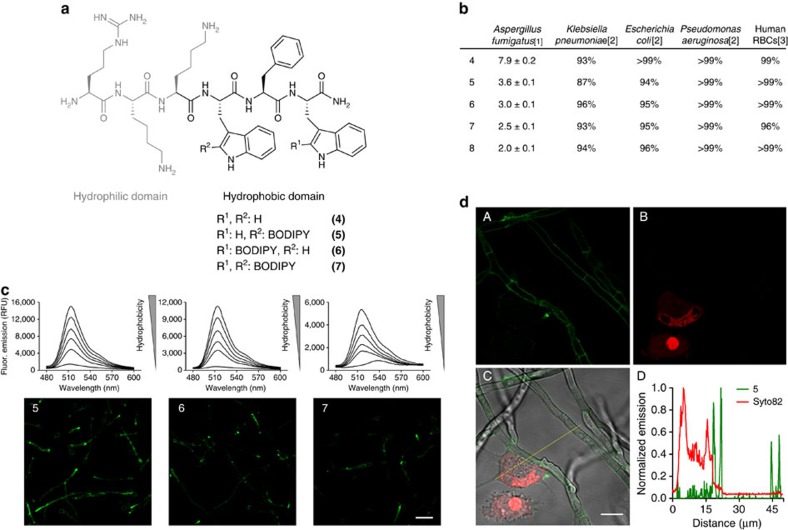
Figure 2. Fluorogenic peptides for live cell imaging of A.fumigatus in co-culture with human lung epithelial cells.
(a) Chemical structures of non-labelled and fluorogenic linear peptides (4-7), highlighting the two conserved hydrophilic (grey) and hydrophobic (black) domains of Peptide Antifungal 26 (PAF26). (b) Activity of antimicrobial peptides in A. fumigatus, several bacterial strains and in human RBCs.[1] IC50 (μM) values represented as means±s.e.m. from n=3, [2] cell viability upon 16 h incubation with 4–8 at their respective IC50 concentrations (n=3), [3] cell viability upon 1 h incubation with 4–8 at their respective IC50 concentrations (n=3). (c) Fluorogenic behaviour of 5–7 (10 μM) in phosphatidylcoline (PC):cholesterol (7:1) liposome suspensions in PBS ranging from 3.75 to 0.004 mg ml−1 of PC in two-fold serial dilutions (λexc.: 450 nm), and wash-free live cell images of A. fumigatus at 37 °C using fluorescence confocal microscopy after incubation with peptides 5–7 (5 μM). Scale bar, 20 μm. (d) Peptide 5 (5 μM, green) and Syto82 (2.5 μM, red counterstain for lung epithelial cells) were incubated in co-cultures of A. fumigatus and human lung A549 epithelial cells and imaged under a fluorescence confocal microscope at 37 °C without any washing steps. Fluorescence staining of 5 (A), Syto82 (B), merged (C) and plot profile analysis (D) of peptide 5 (green) and Syto82 (red) from image C. Scale bar, 10 μm.