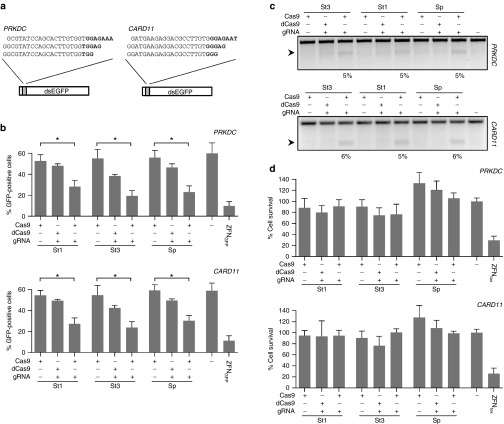
Figure 1.
Activity and cytotoxicity of RGNs. (a) Protospacers of RGNs and episomal GFP reporter. The target sites of the six RGNs used in this study targeting the human PRKDC and CARD11 genes are shown with the corresponding PAM sequences in bold. The indicated PRKDC or CARD11 sequences were cloned in between the start codon and a dsEGFP gene to create a GFP reporter plasmid used to monitor RGN activity. (b) RGN cleavage activity. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with plasmids expressing the RGNs targeted to PRKDC (upper panel) or CARD11 (lower panel), respectively, and the corresponding reporter plasmid. As a negative control, guide RNA (gRNA) plasmids were omitted or the cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing catalytically inactive Cas9 variants (dCas9). The graph shows the amount of GFP-positive cells determined by flow cytometry 48 hours posttransfection as compared to mock transfected cells (−; n = 3). As a positive control, cells were transfected with a GFP-specific zinc finger nuclease pair (ZFNGFP). Statistically significant differences are indicated by an asterisk (*P < 0.05). (c) Episomal cleavage of the reporter plasmid. The reporter plasmid DNA from cells transfected with PRKDC- or CARD11-specific RGNs was extracted and analyzed for evidence of NHEJ-induced indels via the mismatch-sensitive T7 endonuclease I (T7EI) assay. The arrow indicates the expected position of the digestion products. Numbers at the bottom show the average percentage of modified alleles (n = 3). (d) RGN-associated cytotoxicity. Cells were transfected with the same plasmids as in (c) together with a plasmid expressing mCherry. Cell survival is calculated as the fraction of mCherry-positive cells at day 5 as compared to day 2 posttransfection as measured by flow cytometry, relative to a control sample transfected with a plasmid expressing the nontoxic I-SceI meganuclease (n = 3). A toxic ZFN pair harboring a WT FokI cleavage domain was used as control (ZFNtox). Error bars indicate SEM. St1, St3, and Sp refer to RGNs based on Streptococcus thermophilus CRISPR1, CRISPR3, and Streptococcus pyogenes CRISPR-Cas9, respectively. NHEJ, nonhomologous end joining; PAM, protospacer adjacent motif; RGN, RNA-guided nuclease.