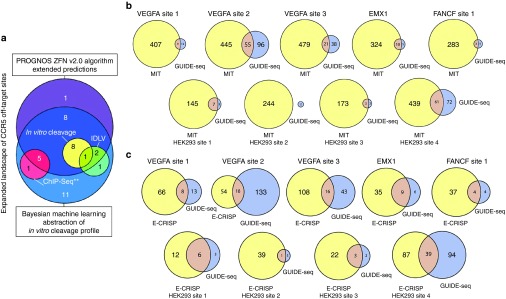
Figure 2.
Comparison of off-target analysis by different methods. (a) The 38 heterodimeric bona fide off-target sites for CCR5 ZFNs42 found by four different experiment-based prediction methods and the refined “ZFN v2.0” PROGNOS algorithm. The PROGNOS sites are drawn from the top rankings spanning 3× the number of predictions by the Bayesian abstraction of the in vitro cleavage profile. (**) Note that only six of the sites found using ChIP-Seq were described,44 so the full degree of overlap of all ChIP-Seq sites with sites found by other methods remains unknown. Adopted from Fine et al.46. (b) A comparison of the off-target predictions by the MIT CRISPR Design Tool (solely bioinformatics-based) to the bona fide off-target sites found for nine different RGENs by the GUIDE-Seq method (experimental-based). (c) A comparison analogous to (b) but using the E-CRISP bioinformatics-based prediction tool. GUIDE-Seq figures adopted from Tsai et al.55.