Figure 1.
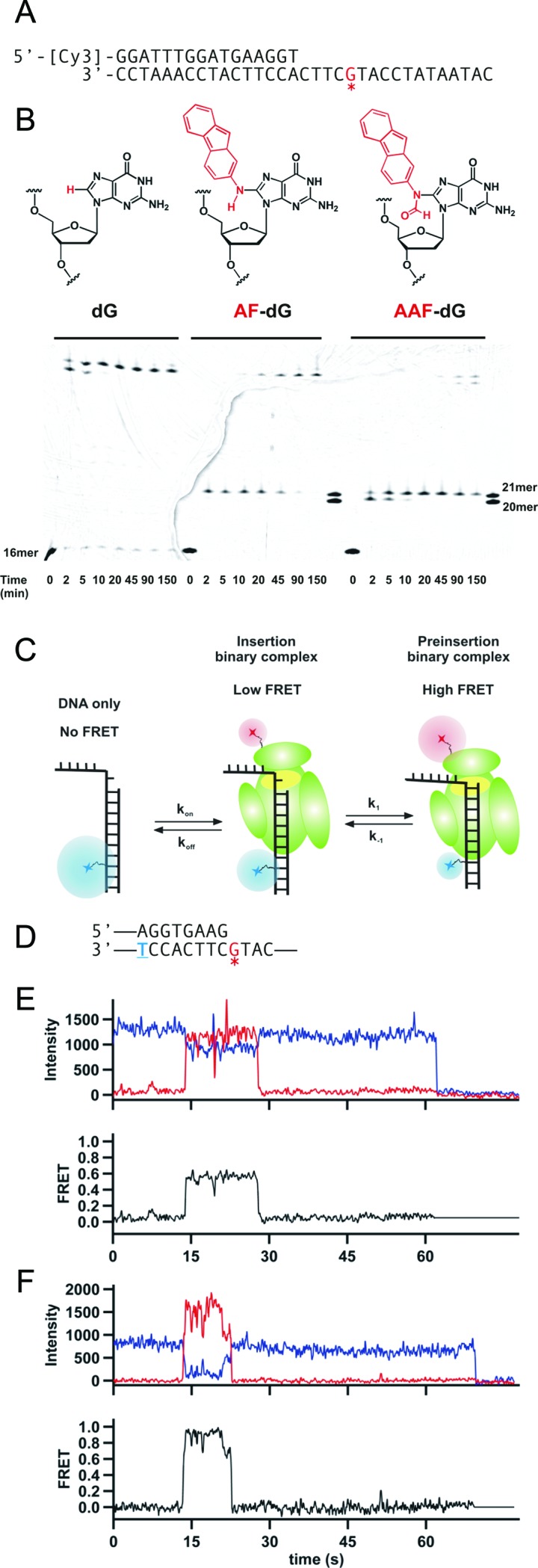
Carcinogenic adducts 2-aminofluoene (AF) and N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene (AAF) induce polymerase stalling at different positions on the DNA. (A) Primer-template sequence used to characterize Dpo4 activity around adduct sites. A Cy3 dye for gel imaging is conjugated at the 5′ end of the primer. The asterisk red G in the template corresponds to either an unmodified deoxyguanosine (dG), N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-2-aminofluorene (AF-dG) or N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene (AAF–dG). (B) Chemical structure of dG (left), AF–dG (middle) or AAF–dG (right). Below the structures a Running start Dpo4 extension assay is shown. Three different reactions were carried out with the indicated primer-templates. Reactions were initiated by addition of polymerase and quenched at the indicated time points by mixing with equal volume of loading buffer (10 mM EDTA, 1 mg/ml bromophenol blue in formamide). A lane to the right of the reactions with carcinogens marks the position before the adduct (20-mer) and the adduct position (21-mer). (C) Schematic of single molecule design and summary of the previously proposed model. Upon polymerase binding, energy is transferred from Cy3 (blue sphere) to the Cy5 on the protein (red sphere). Dpo4 shuttles between two different conformations: an insertion binary complex showing low FRET and a preinsertion binary complex that shows high FRET. (D) Primer-template sequence used in the smFRET studies of Dpo4 binding to DNA. A Cy3 dye is conjugated to the underlined blue thymine, while the asterisk red G contains an AF or AAF adduct. (E) Characteristic single-molecule trace for Dpo4 binding the AF-modified DNA construct shown in (D). Polymerase binding at ∼15 s results in a decrease in Cy3 signal (blue line) accompanied by an increase in Cy5 intensity (red line). The bottom trace shows the FRET efficiency (black) calculated as FRET = IA/(IA + ID). (F) Example trace for Dpo4 binding the AAF-modified DNA construct shown in (D).
