Figure 5.
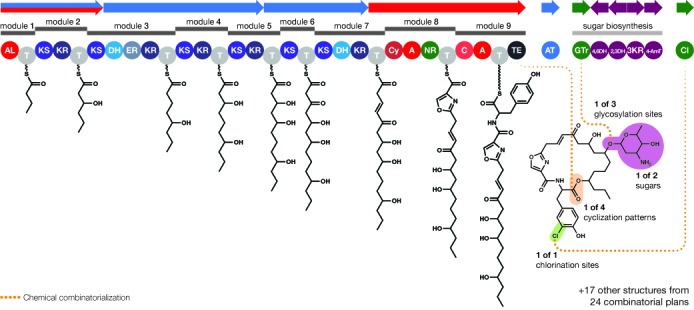
Combinatorial scaffold library generation for a hypothetical biosynthetic gene cluster in PRISM. Biosynthetic modules are identified and the linear scaffold is constructed based on the predicted substrate of the adenylation, acyl-adenylating or acyltransferase domain within each module. Potential deoxysugar combinations and sites of attachment, tailoring reaction substrates, and macrocyclization patterns are identified and combinatorialized. In this hypothetical cluster, two deoxysugars are predicted as potential substrates of the lone glycosyltransferase. The deoxysugar in each combinatorial plan can be added at any of three potential glycosylation sites. Three potential macrolactone cyclizations are identified in addition to the linear carboxylic acid, and a single chlorination site is predicted, producing a total of 24 combinatorial plans. Execution of each combinatorial plan produces a single predicted structure. Combinatorial plans which fail to execute (e.g. when macrocyclization and glycosylation take place at the same free hydroxyl) are discarded.
