Figure 2.
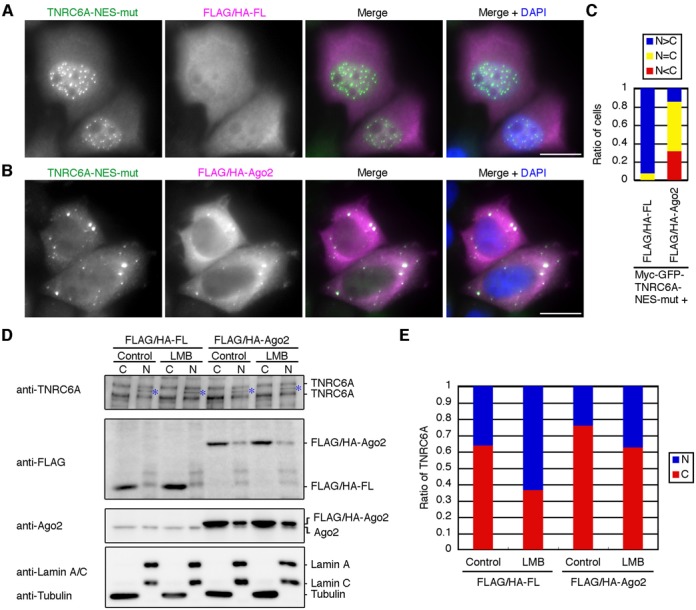
Overexpression of Ago proteins inhibits the nuclear transport of the diffused signals of myc-GFP-TNRC6A-NES-mut and endogenous TNRC6A proteins. (A and B) HeLa cells expressing myc-GFP-TNRC6A-NES-mut with FLAG/HA-FL (A) or -Ago2 (B) were stained with an anti-GFP antibody and an anti-HA antibody, followed by FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG and Cy5-conjugated anti-mouse IgG. Fluorescent images are shown from the left: FITC signals of the second antibody against anti-GFP antibody; Cy5 signals of the second antibody against anti-HA antibody; the merged images of FITC and Cy5, in which FITC is shown in green, the Cy5 in magenta; the merged images with DAPI (blue). Bars, 20 μm. (C) The ratio of cells in which the diffused GFP signals of myc-GFP-TNRC6A-NES-mut in the nucleus were stronger than (N>C, blue), equal to (N = C, yellow), or weaker than (N<C, red) those in the cytoplasm. (D) HeLa cells were inoculated in a well of a 6-well culture plate at 4 × 105 cells/2ml/well at 1 day before transfection. The cells were transfected with FLAG/HA-FL or FLAG/HA-Ago2 plasmid (2.0 μg/well), and re-inoculated at 8 × 105 cells/2ml/well at 1 day after transfection. At 1 day later, the cells were treated with LMB for 8 hr, and fractionated. Fifteen μg of the cytoplasmic fraction (C) or 2.5 μg of the nuclear fraction (N) were analyzed by western blot using an anti-TNRC6A, anti-FLAG, and anti-Ago2 antibodies. Note that HeLa cells endogenously express two isoforms of TNRC6A, ∼210 kDa TNRC6A (NP_055309) and ∼182 kDa TNRC6A (AAK62026) proteins, and that the cytoplasmic fraction was loaded about 1.6-fold compared with the nuclear fraction in each sample. Anti-tubulin and anti-Lamin A/C antibodies were used as a cytoplasmic and a nuclear marker, respectively. Asterisks indicate nonspecific bands. (E) The ratio of signal intensities of TNRC6A proteins between the nucleus (N, blue) and the cytoplasm (C, red). Signal intensities of the bands corresponding to ∼210 kDa and ∼182 kDa TNRC6A in D were measured and added up in each fraction and converted into total signal intensities based on the volume of the loaded fraction, and the nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio of TNRC6A was calculated. The similar results were obtained by two independent experiments.
