Figure 1.
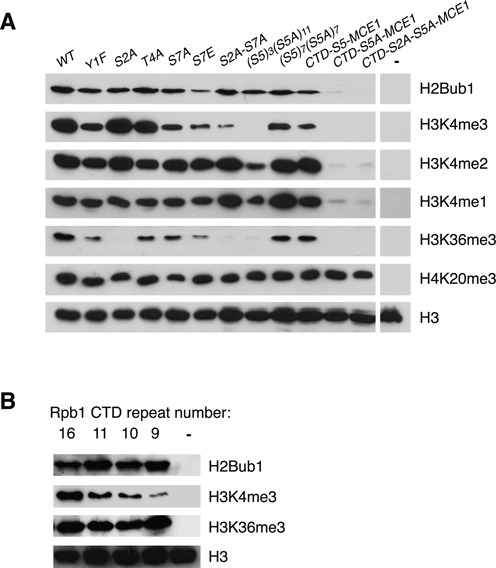
Analysis of the roles of Rpb1 CTD phosphorylation sites in co-transcriptional histone modifications. (A) Whole-cell extracts derived from the indicated rpb1 strains (top) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (right). The ‘WT’ strain expresses a truncated but fully functional form of the CTD containing 14 consensus heptapeptide repeats (rpb1-CTD-14). The mutant strains express CTDs bearing the indicated mutations in all of the consensus repeats. The S5A mutant strains harbor CTDs with the indicated combinations of wild-type and S5A mutant repeats. MCE1 strains express CTDs that are fused to the mRNA capping enzyme MCE1. The last lane on each blot shows an extract derived from a negative control strain (htb1-K119R for H2Bub1, set1Δ for H3K4me, set2Δ for H3K36me3, set9Δ for H4K20me3). (B) As in (A). Shown are immunoblots performed on extracts from strains expressing rpb1 variants with 16, 11, 10 or 9 consensus repeats. The last lane on each blot shows an extract derived from a negative control strain (htb1-K119R for H2Bub1, set1Δ for H3K4me3, set2Δ for H3K36me3).
