Figure 2.
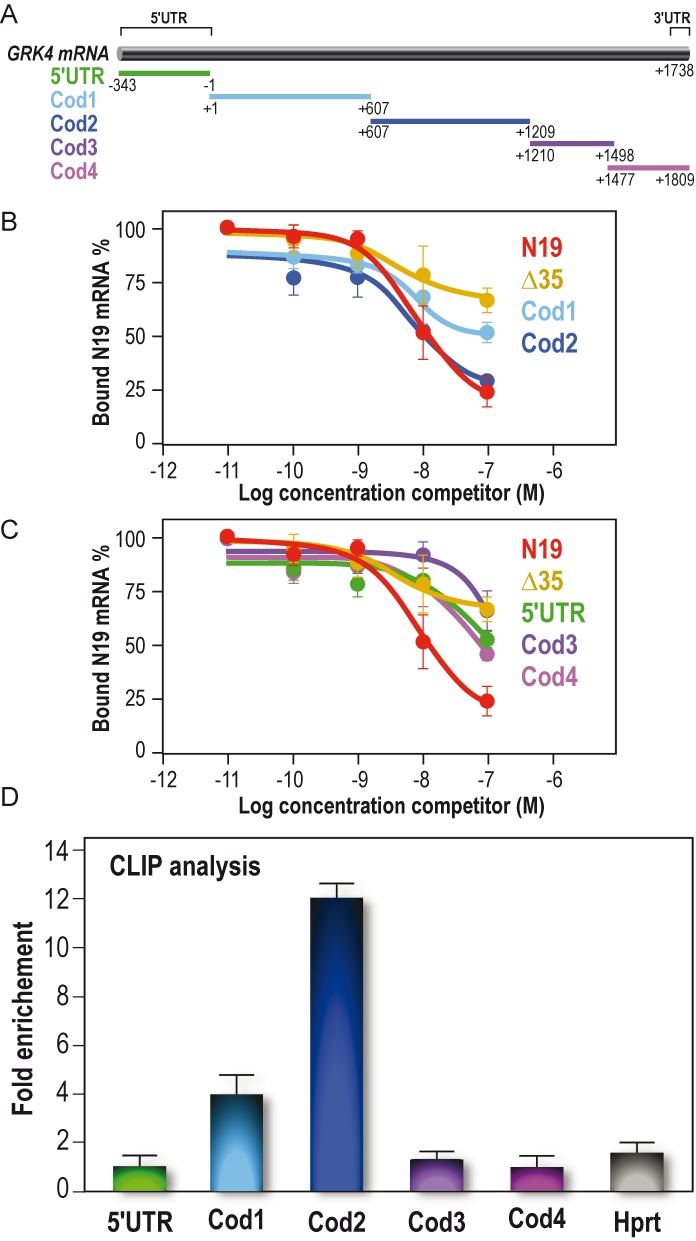
FMRP binds specifically GRK4 mRNA in vitro and in vivo. (A) Schematic representation of human GRK4 mRNA (BC117320) and the fragments subcloned from full-length cDNA and used to map the binding domain of FMRP on GRK4 mRNA. (B) Binding specificity of FMRP to GRK4 mRNA. Filter binding assay was performed by using full-length FMRP and 32P-labeled N19 probe. The competition was performed using various regions of unlabeled GRK4 mRNA: 5′ UTR region, Cod1, Cod2 fragments, N19 itself and Δ35 (the N19 fragment carrying the deletion of the G-quadruplex structure, as shown in Supplementary Figure S2A). The graph depicts the fraction of bound labeled N19 RNA plotted against unlabeled competitor RNA concentration. (C) The same experimental procedure described in (B) but the competition was performed using different regions of unlabeled GRK4, namely Cod3 and Cod4, and the two controls N19 and Δ 35. (D) CLIP analysis experiment. RNA co-immunoprecipitated with FMRP after UV-crosslink, was analyzed by qRT-PCR using specific oligos localized in the GRK4 subdomains we determined for the in vitro analysis. Hprt was used as a negative control. Results are presented as the mean +/− SEM (N = 4).
