Figure 1.
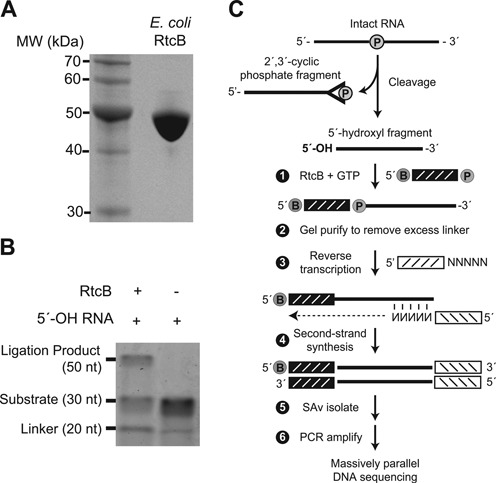
(A) SDS-PAGE analysis of E. coli RtcB protein. Recombinant RtcB protein (10 μg) was electrophoresed through a 10% SDS-PAGE gel and stained with Coomassie blue. (B) RtcB-mediated bimolecular ligation of RNA substrates with 3′-PO4 and 5′-OH termini was analyzed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The ligation product at 50 nt was dependent on RtcB, with an efficiency of ∼25%. (C) Schematic of 5′-hydroxyl (5′-OH) cloning. RNA cleavage generates two fragments with 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate and 5′-OH termini. An adaptor with a 5′-desthiobiotin (B) and 3′-phosphate (denoted by P) is ligated to the 5′-OH RNA fragment with E. coli RtcB ligase. This adaptor has eight randomized positions at its 3′ end which serve as a molecular index to uniquely identify individual ligation events upon sequencing (25). Following ligation, excess adaptor is removed by gel purification. A primer with a 3′ random hexamer region is used for reverse transcription to create cDNA, followed by second-strand synthesis to generated double-stranded DNA products. After streptavidin (SAv) isolation, DNA fragments are PCR amplified and analyzed by Illumina sequencing.
