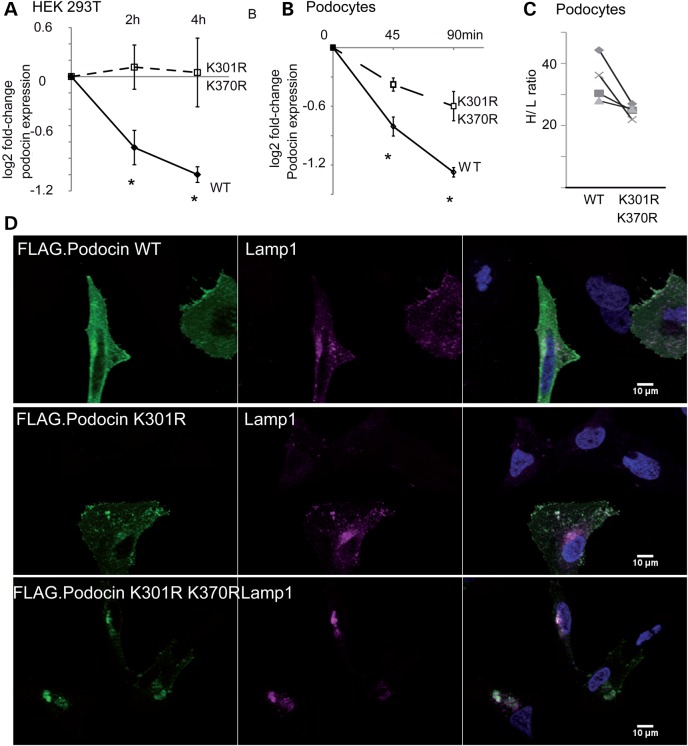
Figure 7.
The Ubr4-dependent residues regulate podocin stability. (A) Measurement of podocin protein stability when expressed in HEK293T cells. Cells were incubated with CHX (c = 100 ng/ml) for the indicated periods. Densitometry quantification of WT and mutant (K301R and K370R) podocin are depicted as logarithmic ratios (n = 5; P < 0.01 in a two-tailed t-test). (B) Measurement of podocin protein stably expressed in podocyte cell lines. Podocytes were incubated with CHX for the indicated periods of time ratios (n = 5; P < 0.01 in a two-tailed t-test). Podocin expression was analysed using immunoblotting for FLAG. (C) Pulse labelling of podocytes with medium containing heavy isotope labelled amino acids. Podocin WT and mutant (K301R/K370R) was purified using an anti-FLAG antibody. Incorporation of heavy isotope labelled amino acids into podocin WT and mutant was measured. Each symbol represents a separate replicate of SILAC ratio quantification per protein. P = 0.05 in a two-tailed t-test. The following 10 peptides were analysed across the experiment: AASESLR, APAATATVVDVDEVR, ARPDAGAER, DMFIMEIDAVCYYR, LGHLLPGR, LPAGLQHSLAVEAEAQR, MAAEILSGTPAAVQLR, SLTEILLER, VALDAVTCIWGIK and VVQEYER. (D) Localization of FLAG-tagged podocin and podocin mutant forms in HeLa cells. Podocin and podocin mutants were transfected in HeLa cells. Podocin was stained using an anti-FLAG antibody. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Podocin with K301R and K301R–K370R substitution colocalized with cotransfected Lamp1, a lysosome marker. Altered podocin localization was independent of co-transfection of Lamp1 (data not shown).