Figure 1.
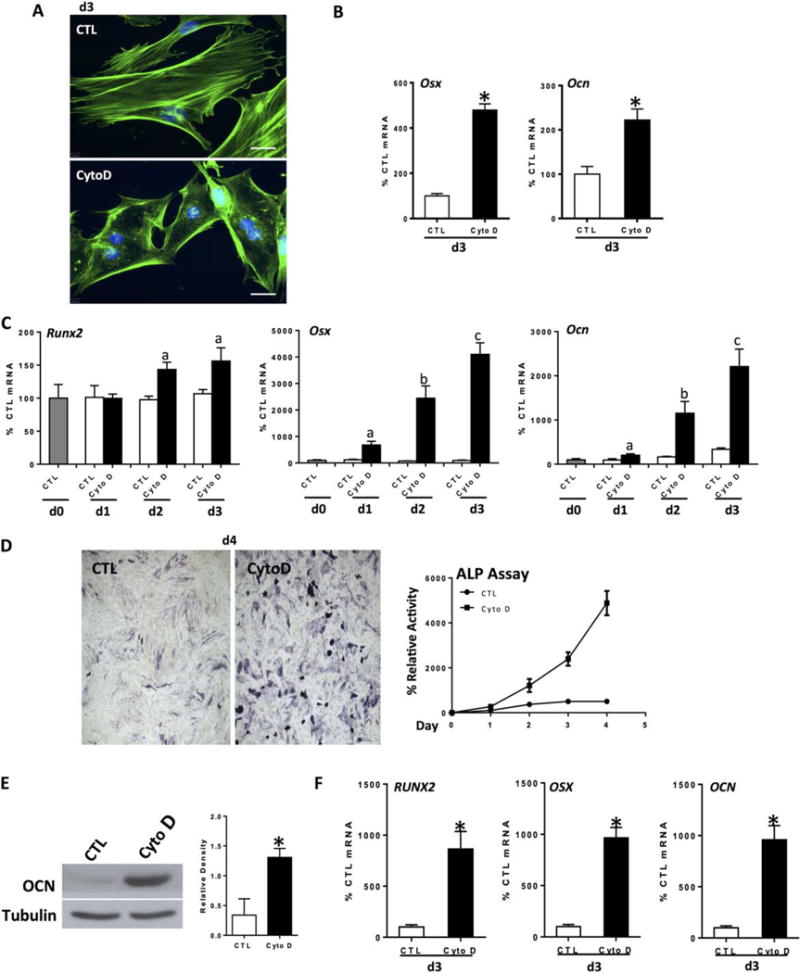
Actin depolymerization initiates and enhances osteogenesis. Mouse marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell (mdMSC) or human marrow-derived MSC (hMSC) were treated with CytoD (0.1 μg/ml) for indicated times. Except for panel (B), cells were cultured in osteogenic medium. (A): Control and CytoD-treated mdMSC stained with phalloidin, day 3. Scale bars = 25 μm. (B): mdMSC cultured in MEM; Osx and Ocn reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. (C): mdMSC response to continuous CytoD, day 3; notations a, b, c ≠ control and differ from each other with p < 0.05. (D): ALP assay (at d1, control without CytoD = 5.1 nmol nNP/μg total protein per minutes) and ALP stain, mdMSC. (E): Osteocalcin (OCN) protein at 5 d, mdMSC. 3 experiments assessed for densitometry of Ocn, shown in graphs to the right, confirm a significant increase; *, p< 0.05. (F): hMSC response to CytoD, 3 days; *, p < 0.01. Abbreviations: ALP, alkaline phosphatase; CTL, control; CytoD, cytochalasin D; OCN, osteocalcin.
