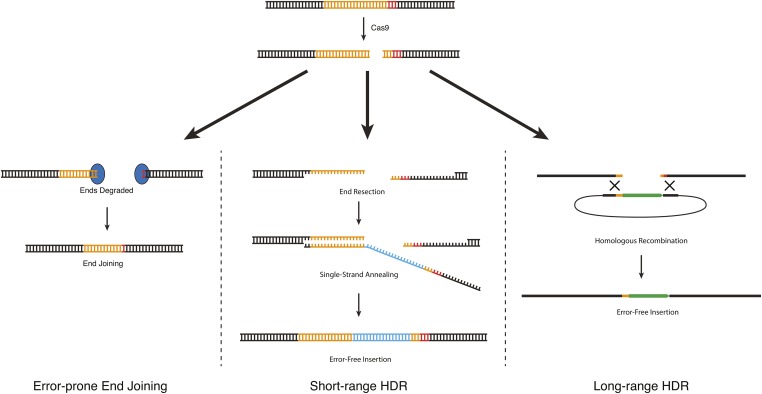
Figure 2.
DNA repair approaches for CRISPR-based genome engineering. DNA double-strand breaks introduced by Cas9 can be repaired via three different mechanisms. End joining produces random insertion/deletion mutations. HDR produces error-free edits using an exogenous DNA molecule as a repair template. Although the mechanisms of HDR in C. elegans are not known, efficiency data suggest the existence of two different HDR pathways (see text). Short-range HDR is hypothesized to occur via a synthesis-dependent strand-annealing mechanism and can accommodate insertions of up to 1–2 kb, with the highest efficiency within 10 bp of the cut site. Long-range HDR is hypothesized to occur via a double-crossover mechanism and can accommodate insertions of at least 12 kb, at distances up to at least 1 kb from the cut site.