Figure 5.
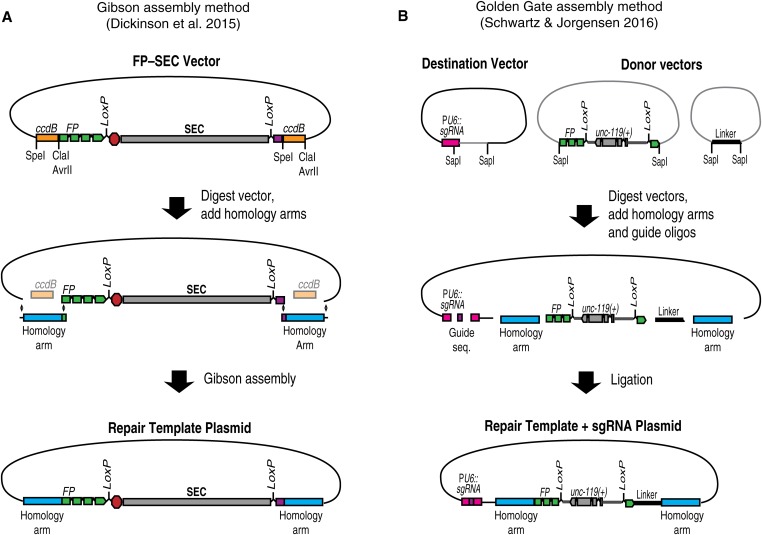
(A) Gibson assembly-based strategy (Dickinson et al. 2015). An FP–SEC vector is digested to release ccdB markers, and homology arms are inserted by Gibson assembly to generate the repair template plasmid. Since the ccdB-containing parent vector does not transform, correct clones make up a majority of transformants and can be identified directly by sequencing. (B) SapTrap assembly strategy (Schwartz and Jorgensen, 2016). Homology arms and the sgRNA sequence are assembled, along with pre-existing tag and selectable marker building blocks, into a destination vector. The Type II restriction enzyme SapI generates unique overhangs that ensure ligation of the various fragments in the correct order.