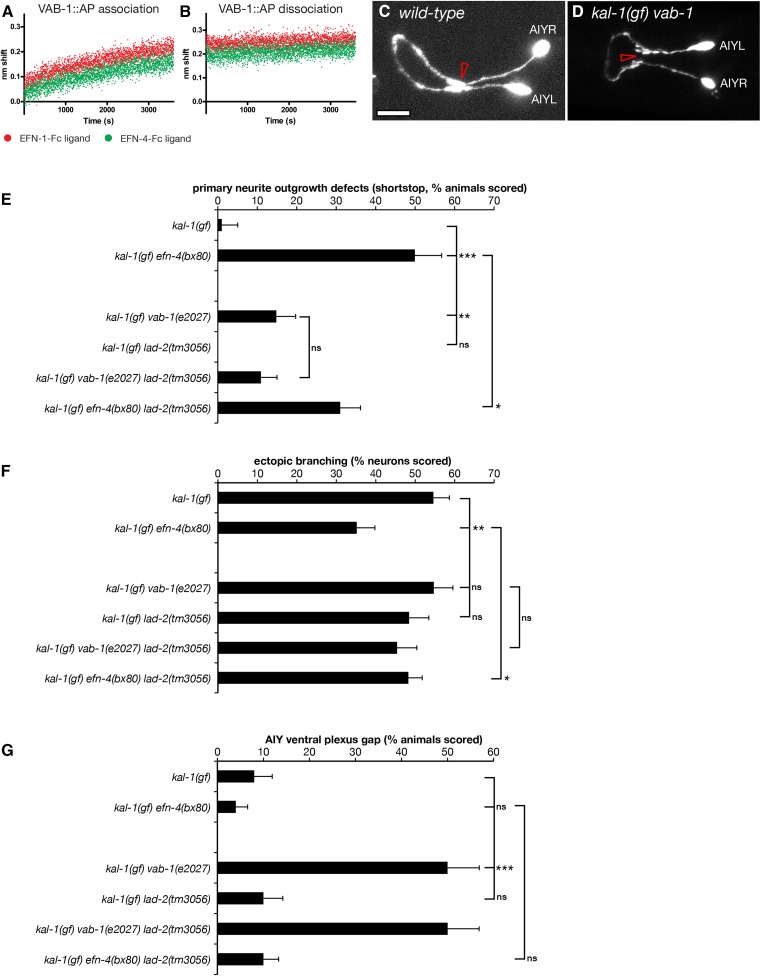
Figure 5.
The Eph receptor vab-1 promotes primary neurite outgrowth and ventral plexus contact in AIY neurons. Biolayer interferometry was used to demonstrate binding between the extracellular domain of VAB-1 fused to alkaline phosphatase and ephrins EFN-1 and EFN-4. (A) VAB-1::AP-binding association phase. (B) VAB-1::AP dissociation phase. Binding curves are normalized against an Fc control to correct for instrument drift. (C and D) Confocal micrographs of AIY neurons in (C) wild-type and (D) kal-1(gf) vab-1(e2027) mutants. Open arrowhead in C shows the ventral contact point in wild-type AIY pairs. (D) vab-1 mutants show a highly penetrant ventral gap where the AIYL/R cells fail to contact each other. Mutations in the candidate EFN-4 receptors vab-1/EphR and lad-2/L1CAM were assayed for (E) primary neurite outgrowth, (F) ectopic axon branching, and (G) ventral plexus contact. Statistical significance was determined using the Z-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Error bars are standard error of proportion.