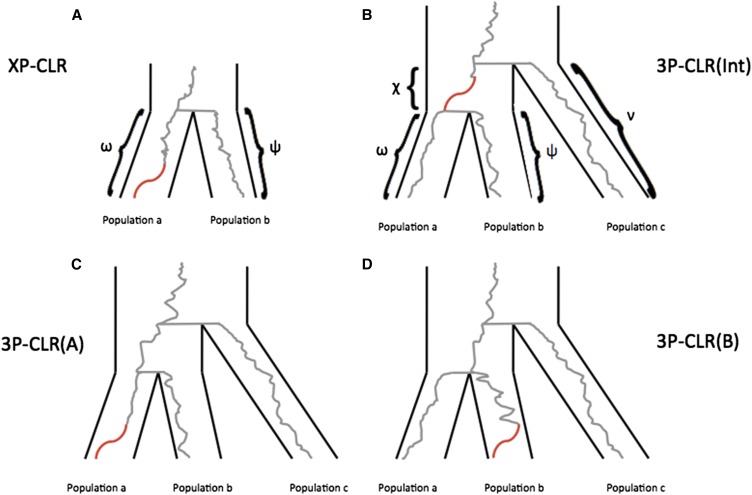
Figure 1.
Schematic tree of selective sweeps detected by XP-CLR and 3P-CLR. While XP-CLR can use only two populations (an outgroup and a test) to detect selection (A), 3P-CLR can detect selection in the ancestral branch of two populations [3P-CLR(Int) (B)] or on the branches specific to each population [3P-CLR(A) (C) and 3P-CLR(B) (D)]. The Greek letters denote the known drift times for each branch of the population tree.