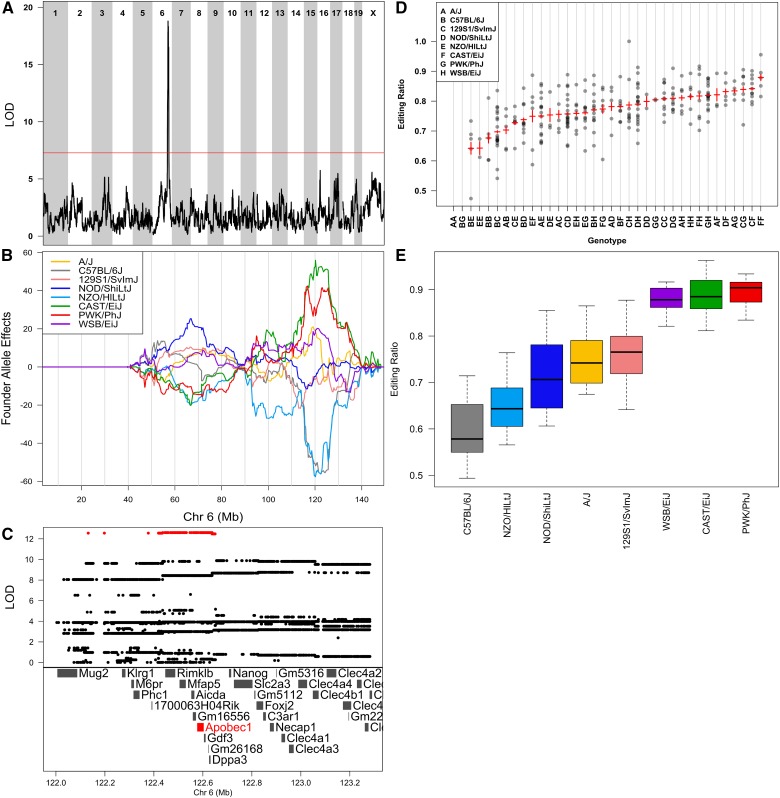
Figure 3.
Genome scan of Apob C-to-U editing shows that editing is regulated by genetic variants on chromosome 6 that overlap Apobec1. (A) Genome scan of Apob editing shows a strong association on chromosome 6. Horizontal axis shows the mouse genome; vertical axis shows the LOD score. Red line is the permutation-derived α = 0.05 significance threshold. (B) Founder allele effect plots for Apob C-to-U editing on chromosome 6. Horizontal axis plots Mb along chromosome 6; vertical axis plots the founder allele effects from the linkage mapping model. Each colored line represents the effect of one of the eight founder alleles along the genome. (C) Association mapping within the QTL support interval shows a band of SNPs with high LOD scores (in red) that cover Rimklb, Mfap5, Aicda, Gm16556, Apobec1, Gdf3, Gm26168, and Dppa3. Apobec1 is highlighted in red because it has been associated previously with Apob C-to-U editing. (D) Genotypes of DO mice at the location of the maximum LOD score (horizontal axis) vs. the editing ratio (vertical axis). DO mice may have one of 36 unphased genotypes, and these are denoted by two letters, each referring to one founder, along the horizontal axis. (E) Apob C-to-U editing ratio in the eight DO founders shows that the editing pattern is similar to the founder allele effects near Apobec1.