Figure 5.
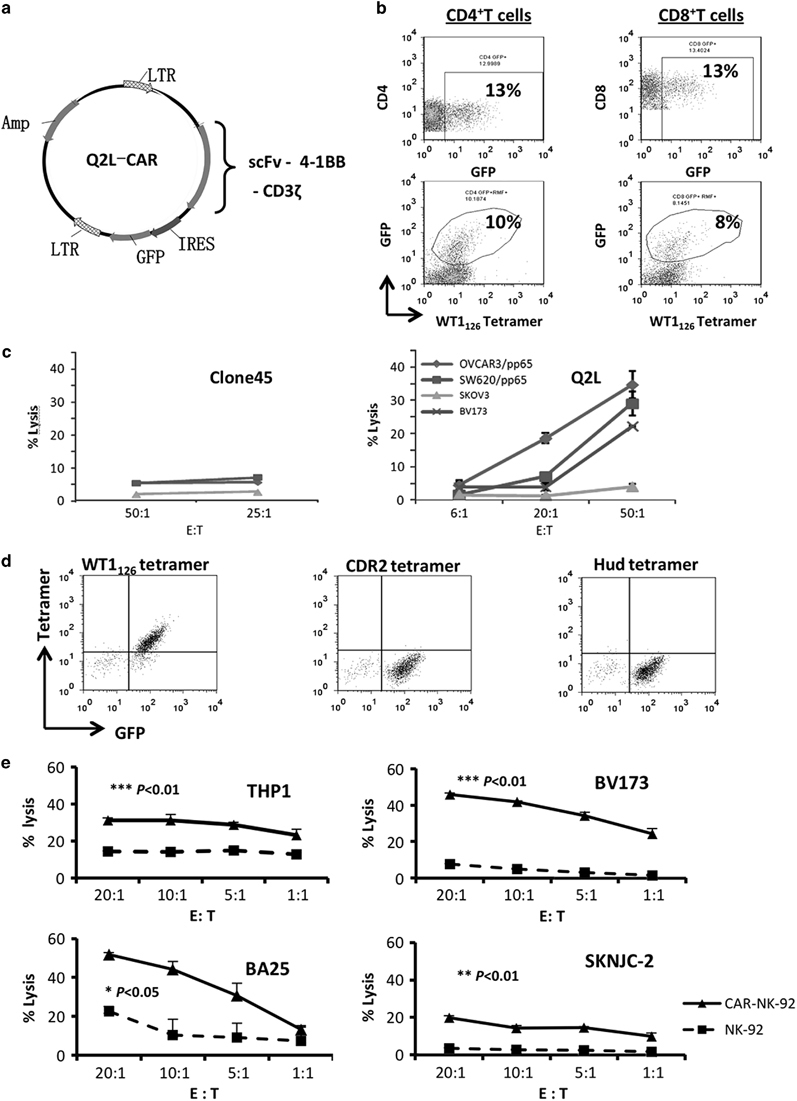
CAR-expressing human lymphocytes specific for HLA-A2-WT1126. (a) Schematic diagram of the CAR construct. The scFv sequence was cloned into the CAR gene and further cloned into a murine stem cell virus-based vector, which contained an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) green fluorescence protein (GFP) sequence along with ampicillin resistance. The resulting CAR was composed of the leader sequence, scFv and hinge region on the extracellular surface, a CD8α transmembrane domain, along with 4-1BB and the CD3ζ chain. (b) Transduced T cells derived from a single healthy donor. Both CD4 and CD8 T cells were genetically modified. CAR-modified T cells were stained with HLA-A2-WT1126 tetramer, anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 and analyzed by flow cytometry. (c) Specific cytotoxicity of Clone45-CAR (left) or Q2L-CAR (right) T cells against the tumor cell lines by chromium release assay. Samples were prepared in triplicate, and values are shown as mean±s.e. Experiment was repeated twice with similar results. (d) CAR NK-92 cells were stained with PE-conjugated HLA-A2/WT1126 tetramer (right) and two isotype controls: HLA-A2/Hud tetramer and HLA-A2/CDR2 tetramer. (e) Specific cytotoxicity of Q2L-CAR NK-92 (solid line) and mock (dashed line) cells against the tumor cell lines by chromium release assay. Samples were prepared in triplicate, and values are shown as mean±s.d. Experiment was repeated twice with similar results. The P-values of the difference between CAR and mock groups were analyzed by log-rank Mantel–Cox test, with treatment groups showing similar variance.
