FIGURE 3.
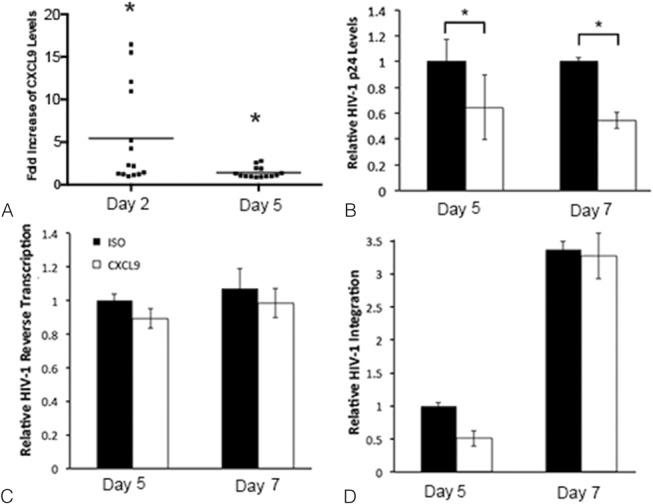
HIV-1 induces CXCL9 expression and blocking CXCL9 decreases HIV-1 replication in PBMCs. CXCL9 levels in HIV-1–infected PBMCs were measured on days 2 and 5 after infection (A). The results from 7 individual experiments evaluated in duplicate are shown. For each experiment, CXCL9 levels were expressed as fold increase in HIV-1–infected cells compared with uninfected controls set to 1. *P < 0.05 for HIV-1–infected vs. uninfected PBMCs. HIV-1 p24 (B) expression, HIV-1 reverse transcription (C) and viral integration (D) were measured in HIV-infected PBMCs treated with CXCL9 neutralizing (CXCL9) or isotype control (ISO) abs on days 5 and 7 after infection. At both time points, HIV-1 p24 levels in CXCL9 neutralizing ab treated tissues were expressed as fold decrease compared with ISO-treated PBMCs set to 1. For HIV-1 reverse transcription and integration, all data were normalized to human β actin. Day 5 values in ISO-treated tissues were set to 1. Day 5 values in CXCL9 neutralizing ab treated tissues or day 7 values in ISO or CXCL9 neutralizing abs treated tissues were normalized to 1. Data are shown as the mean ± SD of 3 experiments with each condition tested in triplicate. *P < 0.05 for CXCL9 neutralizing vs. ISO abs.
