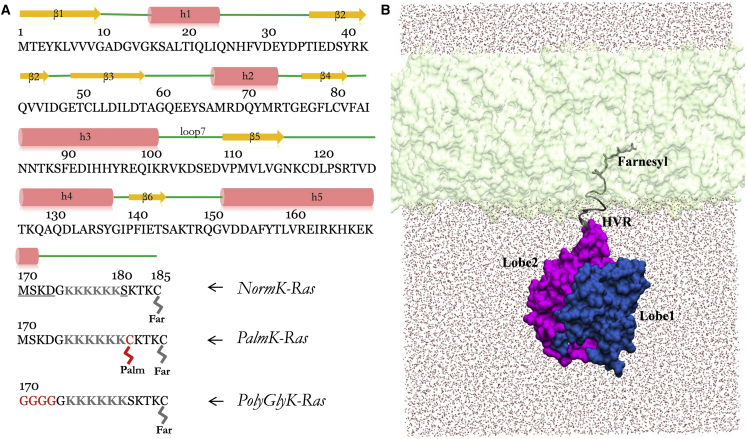
Figure 1.
Sequence and structure of K-Ras and simulation setup. (A) Primary and secondary structure of G12D K-Ras, with structural elements shown in orange (β-strand), red (α-helix), and green (loop region). NormK-Ras refers to the unmodified G12D K-Ras in the GTP-bound form. Underlined residues were mutated and highlighted in red: S181 was mutated to a palmitoylated Cys in PalmK-Ras; residues 170–173 were mutated to Gly in PolyGlyK-Ras. Simulations in the NocmapK-Ras group are the same as in NormK-Ras with the only difference being application of CMAP dihedral correction in the latter but not the former. The hexa-lysine stretch (residues 175–180) and farnesyl are highlighted in gray. Lobe 1 encompasses residues 1–86 and lobe 2 residues 87–166. (B) Starting structure of the full-length farnesylated G12D K-Ras embedded in a POPC/POPS bilayer (light green), with lobe 1 in blue, lobe 2 in pink, HVR and farnesyl in gray and water shown as red dots. To see this figure in color, go online.