Figure 7.
Increased Extracellular α-Synuclein in Heterozygous GBA-N370S-Derived Dopaminergic Neuronal Cultures
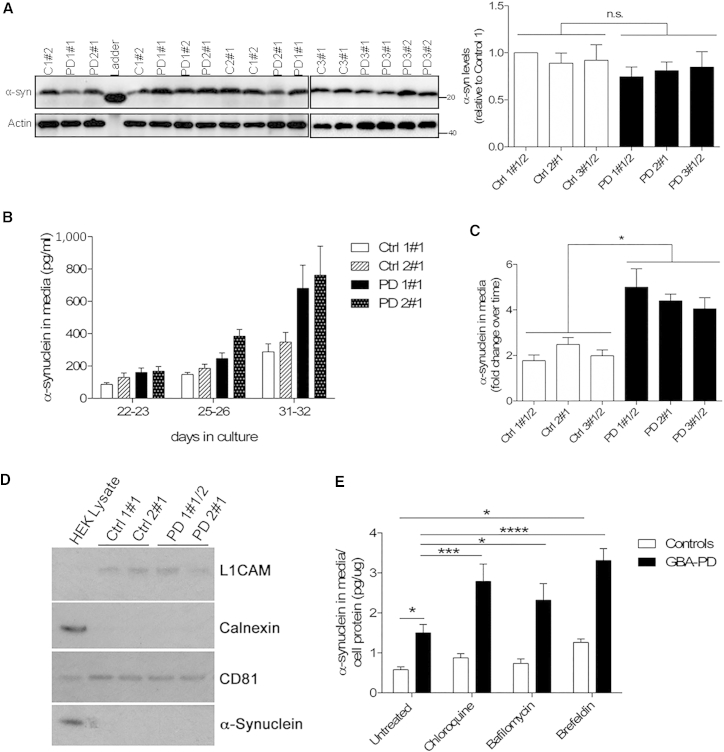
(A) There is no difference in the intracellular α-synuclein content in dopaminergic neuronal cultures from controls and GBA-N370S PD lines. Representative western blot and quantification for intracellular α-synuclein levels.
(B) Analysis of culture media by ELISA revealed the presence of α-synuclein, which increased over time.
(C) Levels of extracellular α-synuclein in culture media were higher for heterozygous GBA-N370S dopaminergic cultures when compared with controls, during maturation, measured by ELISA. Fold change of neurons at day 31–36 compared with early neurons at day 21. In each case, data represent the mean ± SEM from performing at least three independent differentiation experiments per line each analyzed in triplicate. Student's t test; ∗p < 0.001.
(D) Western blot analysis of culture media extracted exosomes confirmed the expression of CD81 and L1CAM exosomal markers in the absence of calnexin. Data represent the mean of replicates ± SEM from performing at least three independent differentiation experiments per line.
(E) Modulation of α-synuclein release in differentiated dopaminergic neurons from control and GBA-N370S dopaminergic cultures by treatment with CQ, bafilomycin A1, and brefeldin A, measured by the MesoScale Discovery platform. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of differentiated lines from at least three independent individuals done in duplicate (n = 6–8). Two-way ANOVA; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.005; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
See also Figure S6.