Fig. 3. Depletion of IFT88 blocks cilia formation in lens epithelial cell explants but does not prevent polarised localisation of basal bodies during fibre differentiation.
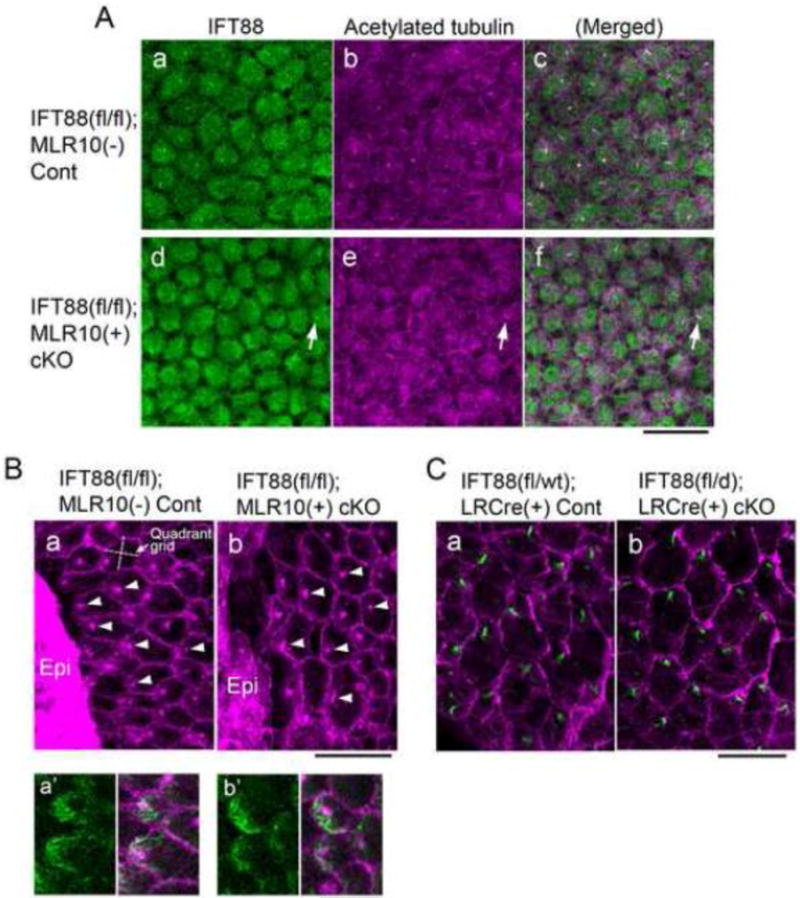
(A) Immunostaining of IFT88 (a, d, green) and acetylated α-tubulin (b, e, purple) of lens epithelial explants prepared from control (a–c) and IFT88 cKO (d–f) neonates (c and f show merged image of a and b, and d and e, respectively). In cKO explants most of the epithelial cells were devoid of cilia and only a few cells were positive for IFT88 and acetylated α-tubulin staining (d–f, arrows). Note that the low level of cytoplasmic staining for IFT88 was non-specific since it was also detected in cKO cells. (B) Immunostaining for β-catenin (signal was localised to cell boundaries) and pericentrin (signal localised basal bodies) in the epithelial explants prepared from lenses of neonates that were cultured for 8 days with 50 ng/mL FGF to induce fibre differentiation. Most cells differentiated into fibre cells with characteristic hexagonal profiles but some cells remained undifferentiated and formed epithelial islands (Epi). The basal bodies at the apical surfaces of the elongating fibres were polarised towards an epithelial island in most cells of control (a) and IFT88 cKO (b) explants. The orientation of the quadrant grid in each cell was related to the direction of the nearest epithelial island (an example gird is shown in a). In these elongating fibres polarised accumulation of acetylated α-tubulin (green in a′, control and b′, cKO) was located at the migrating front of the apical surface of each fibre. (C) Immunostaining for rootletin (green) localised the ciliary rootlet that extends from the basal body and forms part of the basal body at the apical surface of each of the fibres of control (a) and IFT88 cKO (b) lenses (5-week-old). β-catenin staining (purple) delineates the hexagonal boundaries of fibre cells. The anterior pole and the equator of each lens locate to the top and the bottom of the images, respectively. The cilia/basal bodies in both control and cKO lenses showed polarised localisation to the anterior side of the hexagonal apical surface of the fibres. Scale bars: A–C 20 μm; Ba′, b′ 10 μm.
