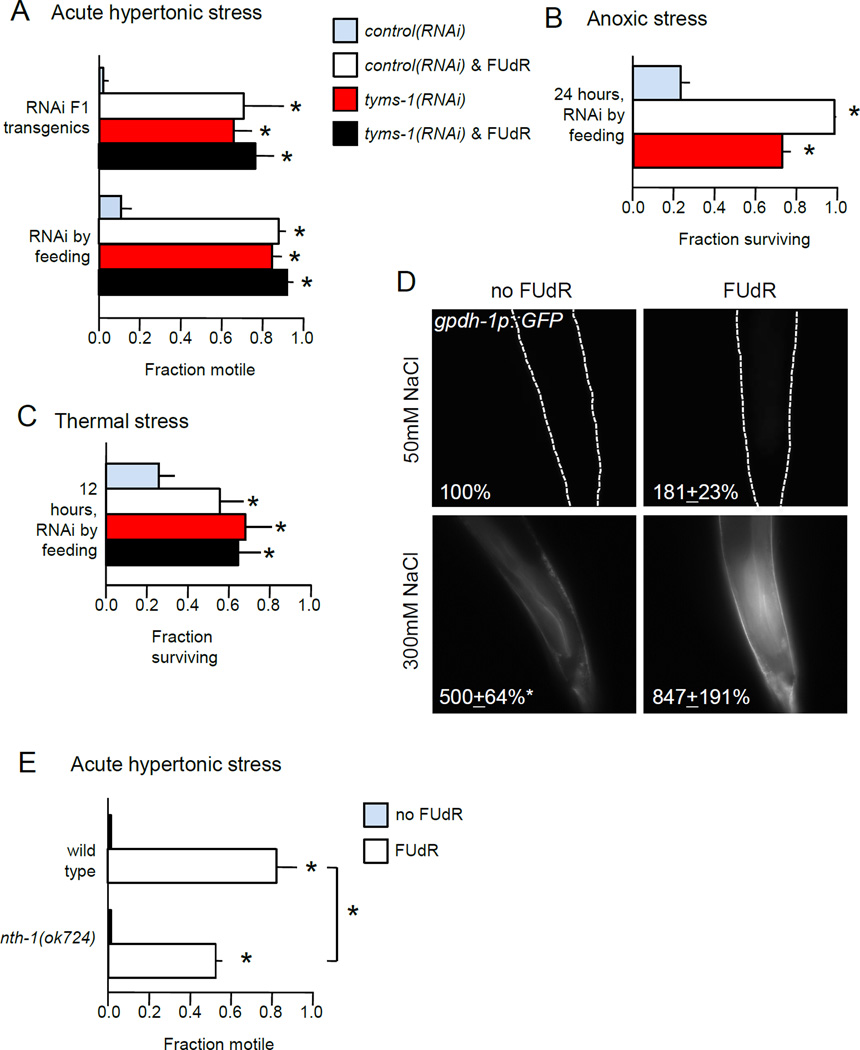
Figure 4. Thymidylate synthase inhibition induces broad stress resistance.
A. FUdR or tyms-1(RNAi) increases resistance to acute hypertonic stress. Fraction of motile animals was measured 10 minutes after transfer to 500 mM NaCl plates. n = 3 independent replicate experiments, with 30 animals per replicate.
B. FUdR increases resistance to anoxia. Fraction surviving anoxia in BioBag was assessed at 24 hours. n = 3 independent replicate experiments, with at least 20 animals per replicate.
C. FUdR confers resistance to thermal stress. Fraction surviving was assessed after 12 hours at 35°C. n = 4 independent replicate experiments, with at least 28 animals per replicate.
D. Either FUdR treatment or hypertonic stress induced expression of gpdh-1p::GFP. Average percent change in GFP fluorescence for gpdh-1::GFP at rear of intestine after 48 hours in 3 replicate experiments, with 10 animals per replicate. Dotted lines show outline of animal (top panels).
E. nth-1 loss partially abrogates FUdR-mediated resistance to acute hypertonic stress. n = 4 independent replicate experiments, with 30 animals per replicate.
Young adult animals were pre-treated with 400 µM FUdR or bacteria expressing tyms-1(RNAi) for 48 hours prior to stress assays. Error bars indicate SEM, * indicates p < 0.05, n.s. indicates p > 0.05 in Student’s T-test vs. control or between indicated groups.