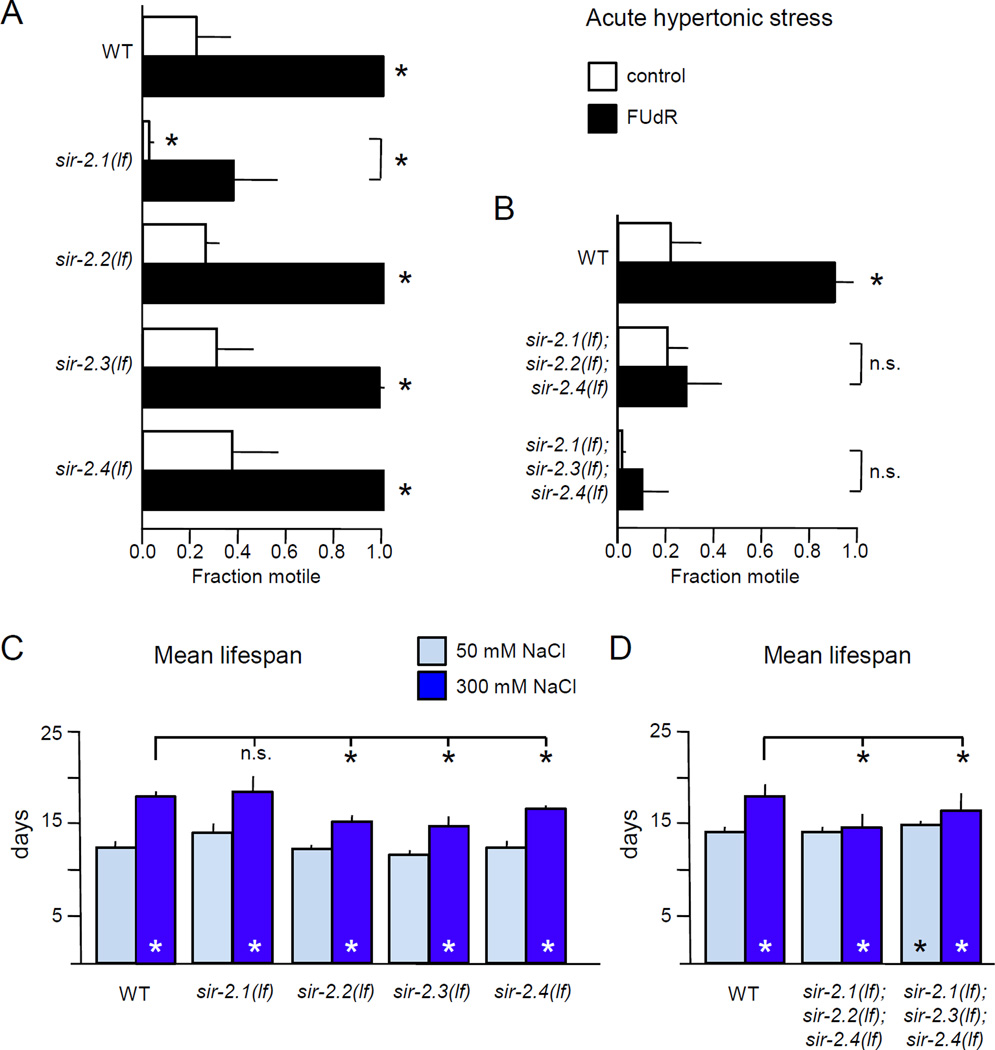
Figure 5. Sirtuin function is required for FUdR to induce stress resistance or increase lifespan.
A. sir-2.1 plays a role in FUdR-induced hypertonic stress resistance. Animals lacking sir-2.1 were hypersensitive to acute hypertonic stress; the effect of FUdR pre-treatment was reduced compared to wild type. Hypertonic stress resistance and FUdR response of animals lacking other sirtuin genes was normal. n = 3 independent replicate experiments, with 45 animals per replicate.
B. Simultaneous loss of three sirtuin genes eliminated the ability of FUdR to induce acute hypertonic stress resistance. For either triple mutant strain, FUdR had no impact on hypertonic stress resistance. n = 5 independent replicate experiments, with at least 34 animals per replicate.
C. Loss of sir-2.1, sir-2.2, sir-2.3, or sir-2.4 did not prevent lifespan extension by FUdR and hypertonic stress. Pooled analysis of three independent replicates at 25° with 400 µM FUdR, for a total of n ≥ 253 animals per condition.
D. Sirtuin function is required for FUdR-induced lifespan extension under hypertonic stress. Loss of three sirtuins partially abrogated lifespan extension induced by FUdR and hypertonic stress. Pooled analysis of three independent replicates at 25° with 400 µM FUdR, for a total of n ≥ 193 animals per condition.
For stress resistance experiments, young adult animals were pre-treated for 48 hours with 400 µM FUdR prior to stress assays. Error bars indicate SEM, * indicates p<0.05 vs. control or between designated columns using Student’s T-test for stress assays and the log-rank test for lifespan.