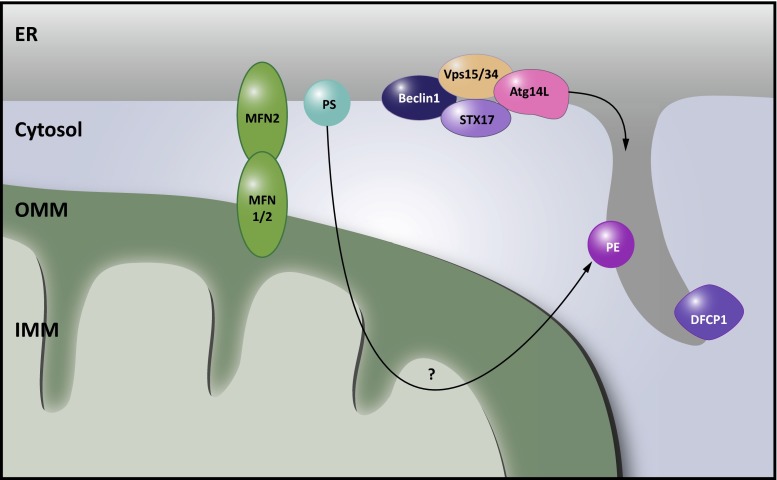
Fig. 6.
MAMs as sites for autophagosome biogenesis. Mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs) were identified as a membrane source for autophagosome biogenesis. In a first instance, phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) synthesis at MAMs was believed to be a crucial lipid source for these emerging organelles. However, ER-mitochondria contact sites appear to play a more direct role. Syntaxin 17 (STX17) at MAMs recruits early autophagosome markers including Atg14L, Vps15, Vps34 and Beclin1. In addition, the omegasome marker double FYVE-containing protein 1 (DFCP1) translocates to these sites upon autophagy induction. Underscoring the relevance of ER-mitochondria membrane contact sites (MCSs), loss of phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein 2 (PACS2) or mitofusin 2 (MFN2) abrogates autophagosome biogenesis