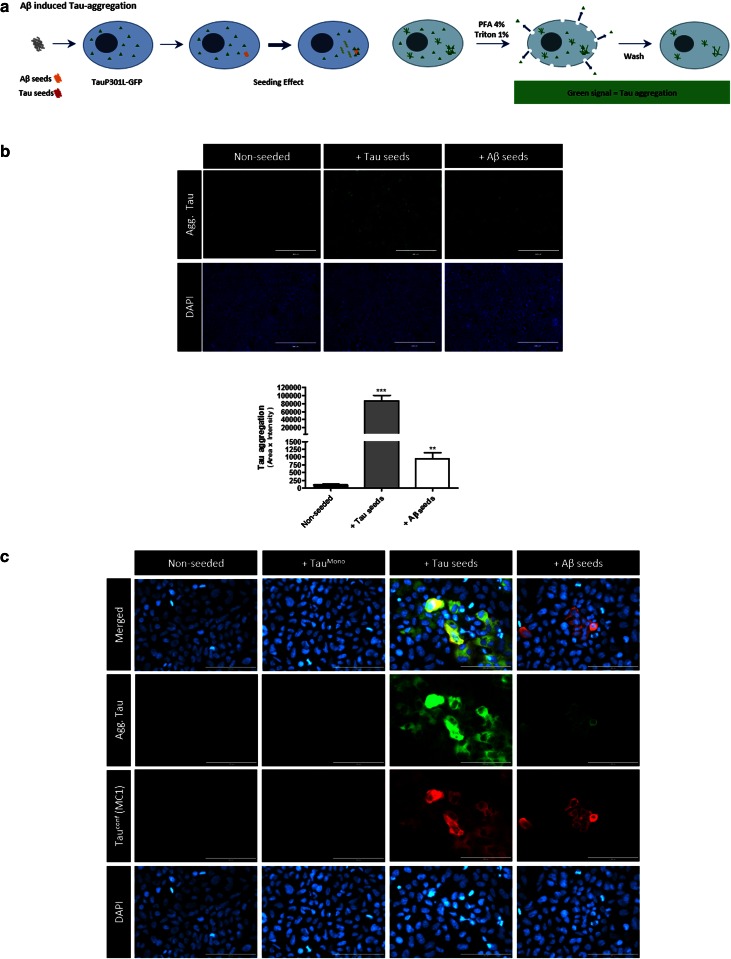
Fig. 1.
Pre-aggregated Aβ-seeds induce Tau-aggregation in a well-characterized in vitro Tau-aggregation assay. a Schematic design of seed induced Tau-aggregation in QBI-293 cells expressing TauP301L-GFP. Pre-aggregated Tau-seeds or Aβ-seeds are added to the cells thereby bypassing the slow nucleation-dependent lag phase. Following stringent extraction using 1 % TX-100 during PFA fixation, soluble forms of Tau are eliminated. The remaining GFP signal represents aggregated GFP-tagged TauP301L. b Similar to Tau-seeds, Aβ-seeds induce Tau-aggregation in the in vitro Tau-aggregation assay, albeit less efficiently than Tau-seeds (scale bar 400 µm). Quantitative analysis reveals significant Aβ-seed induced Tau aggregation (n ≥ 30 fields per condition; Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post hoc test, indicating significant difference compared to non-seeded condition; mean ± SEM are presented; **p value <0.01, ***p value <0.001). c Higher magnification images of the different conditions are presented. Aggregated Tau is stained with MC1 antibody, detecting conformationally altered Tau, further confirming the seed induced Tau pathology, absent in non-seeded cells, and not significantly induced in cells treated with monomeric Aβ forms or monomeric Tau forms (Fig. S2) (scale bar 100 µm)