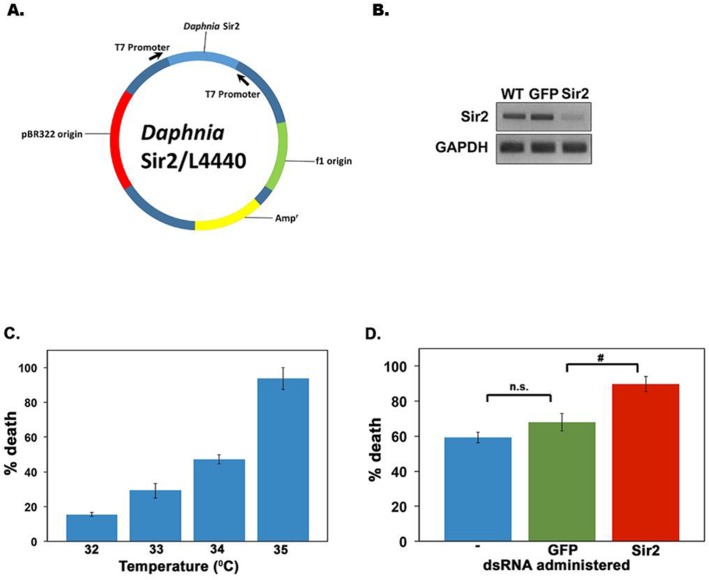
Figure 6. Targeted RNAi knockdown of D. pulicaria Sir2 severely impairs HSR and survival.
(A) Diagram of Sir2 targeting construct. (B) Sir2 transcript levels are diminished following an RNAi feeding regimen of bacteria expressing sir2 dsRNA. Total RNA was isolated from untreated, GFP dsRNA treated, or Sir2 dsRNA-treated Daphnia after the RNAi feeding regimen for ten days. Reverse transcriptase-PCR was performed for 27 cycles with Sir2 or GAPDH specific primers and the product was analyzed on a 1% agarose gel. (C) Mean percentage death following a heat shock in D. pulicaria. D. pulicaria were heat shocked at various temperatures as indicated for 30 minutes, allowed to recover for 24 hours, at which point the percentage death was measured. Error bars represent standard deviations. (D) Mean percentage death in response to heat shock following Sir2 knockdown. After ten days on an RNAi feeding regimen, untreated D. pulicaria (labeled -; blue bar), GFP dsRNA treated D. pulicaria (green bar), and Sir2 dsRNA treated D. pulicaria (red bar) were subjected to heat shock at 340 C for 30 minutes, allowed to recover for 24 hours, and the percentage death was measured. We performed RNAi in a total of 30 individuals per treatment group (for a total of 90 individuals in the experiment) over the course of 4 biological replicates. Error bars represent standard deviations. An ANOVA was performed (F: 146, df: 2,9, p:1.35×10−7) followed by a post hoc Tukey test, # indicate differences between the means at p < 0.5.n.s.: not significant.