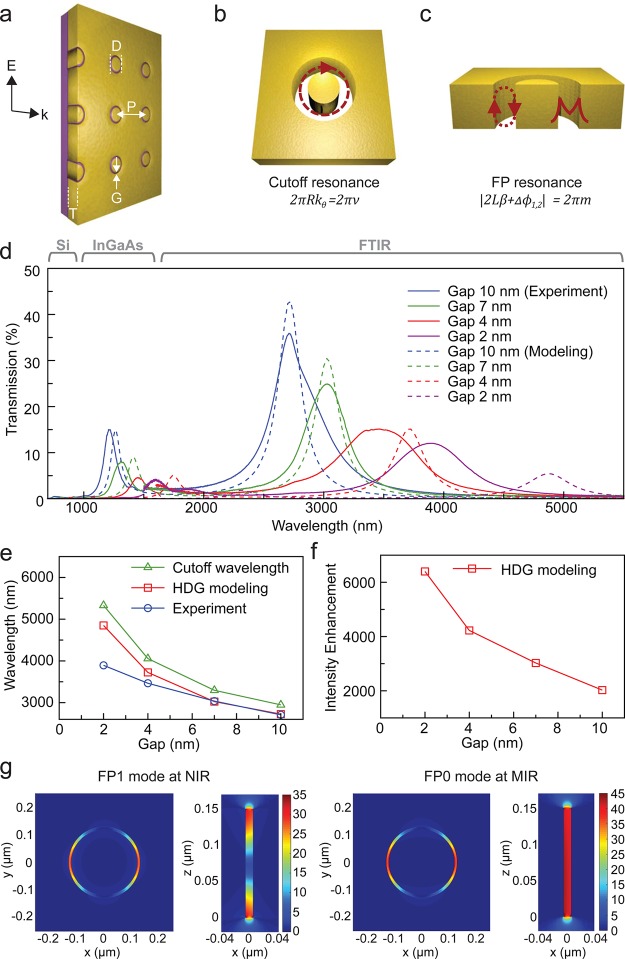
Figure 2.
Extraordinary transmission through the coaxial aperture array. (a) Schematic of a coaxial aperture array. Illumination is through a sapphire substrate with unpolarized light, and transmission spectrum is measured using three different spectroscopic systems covering over three full octaves from 400 to 5000 nm in wavelength. (b,c) Schematics of coaxial waveguides with the cutoff resonance and the FP resonance. (d) Measured and simulated spectra of light transmitted from the coaxial aperture array with a 250 nm diameter and four different gap widths (2, 4, 7, 10 nm). (e) Variation of transmission peak wavelength of the FP0 (m = 0) resonance as a function of gap width in the coaxial aperture array. (f) Intensity enhancement for the FP0 resonance as a function of gap width. (g) Calculated electric field distributions of 250 nm diameter coaxial aperture with a 10 nm gap at the resonance wavelengths of 1200 and 2700 nm.