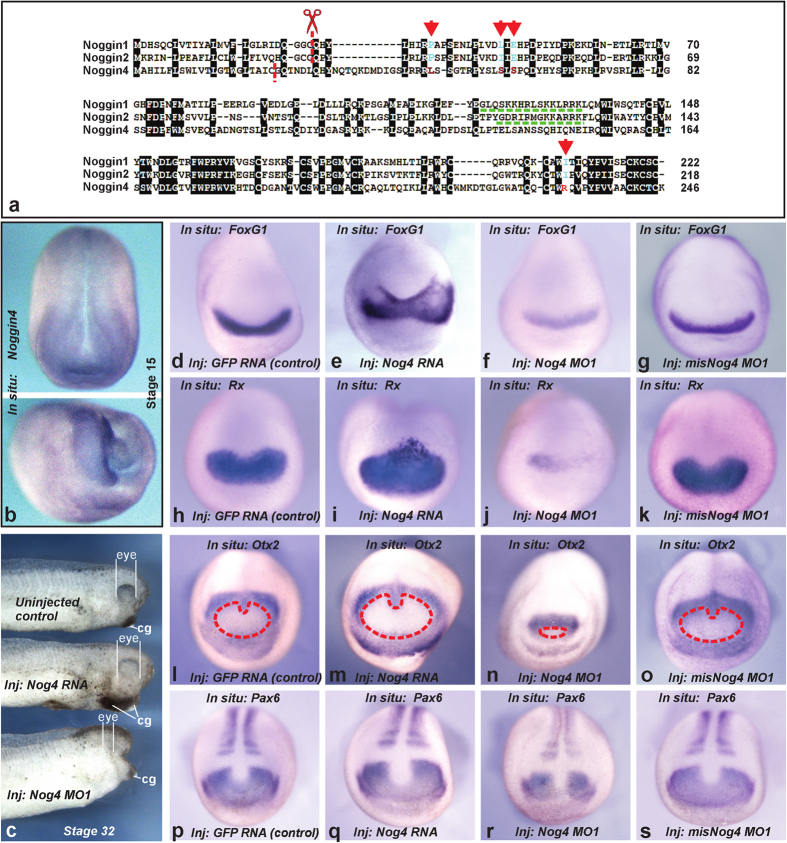
Figure 1. Properties of Noggin4.
(a) Alignment of Xenopus laevis Noggins. Positions essential for Noggin1 binding to BMP1 are indicated by red arrows. HSPG binding motifs and cleavage sites are indicated by green and red dashed lines, respectively. (b) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of a midneurula embryo with dig-probe to Noggin4 mRNA. Dorsal view at the top, the right-frontal view at the bottom. (c) Effects of Noggin4 mRNA (80%, n = 120) and MO1 (85%, n = 130) injections on the development of head structures. Cg-cement gland. (d–s) In situ hybridization with dig-probes to FoxG1, Rx, Otx2 and Pax6 mRNA of midneurula embryos injected with GFP mRNA (control) (0%, n = 40; 0%, n = 50; 0%, n = 40; 0%, n = 30, abnormal phenotypes respectively), Noggin4 mRNA (85%, n = 30; 61%, n = 35; 81%, n = 40; 65%, n = 40 abnormal phenotypes respectively), Noggin4 MO1 (90%, n = 50; 86%, n = 40; 60%, n = 40; 60%, n = 40, abnormal phenotypes respectively) and misNoggin4 MO1 (control) (0%, n = 30; 0%, n = 30; 0%, n = 40; 0%, n = 30, abnormal phenotypes respectively). Red dashed line surrounds the presumptive rostral forebrain territory. Anterior view, dorsal to the top.