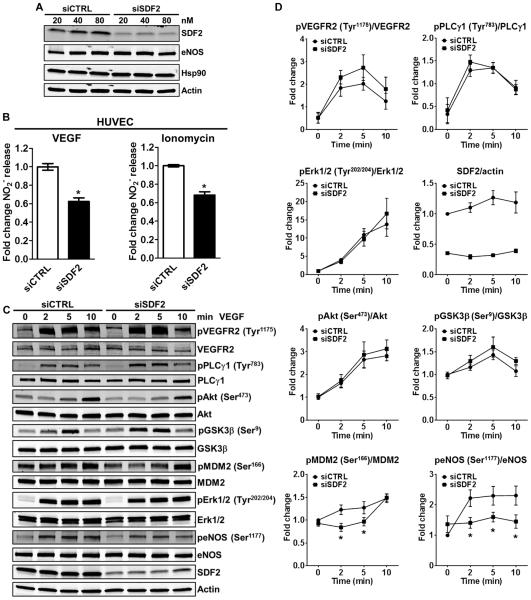
Fig. 2. SDF2 is necessary for eNOS-dependent NO release and phosphorylation of eNOS at Ser1177.
(A) Immunoblot analysis shows the abundance of SDF2, eNOS, and Hsp90 in HUVECs after transfection with 20 to 80 nM control siRNA (siCTRL) or siRNA targeting SDF2 (siSDF2). Actin was used as a loading control. n = 3 independent experiments. (B) Bar graphs illustrate the averaged measurements of NO (NO2−) released by siCTRL or siSDF2 HUVECs after stimulation with VEGF (left) or ionomycin (right); n = 4 independent experiments. (C and D) Representative immunoblot analyses (C) and averaged densitometric data (D) show the effects of SDF2 knockdown on the VEGF-induced dynamic phosphorylation (p) of VEGFR2, PLCγ1, Akt, GSK3β, MDM2, Erk1/2, and eNOS over a time course of 10 min in HUVECs. Actin was used as a loading control. Data are means ± SEM. n = 5 to 10 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 compared to siCTRL.