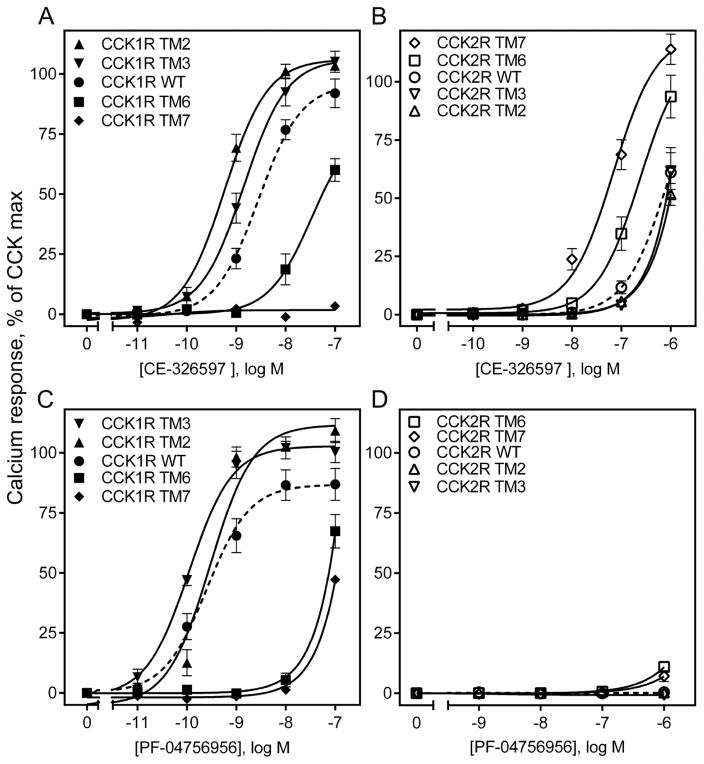
Figure 4. Biological activity at CCK1R- and CCK2R-based chimeric receptor constructs.
The curves shown here are representative of the abilities of CE-326597 (top row) and PF-04756956 (bottom row) to stimulate intracellular calcium responses in the CCK1R (A, C) or CCK2R (B, D) wild type and chimeric constructs bearing CHO cells. The X-axis values reflect the absence of ligand (0) to the left of the break, and log molar concentrations to the right of the break. Data are represented as percentages of the maximal responses of each cell line to 10 nM concentration of natural agonist, CCK. Data are expressed as means ± S.E.M. of duplicate determinations from at least three to nine independent experiments.