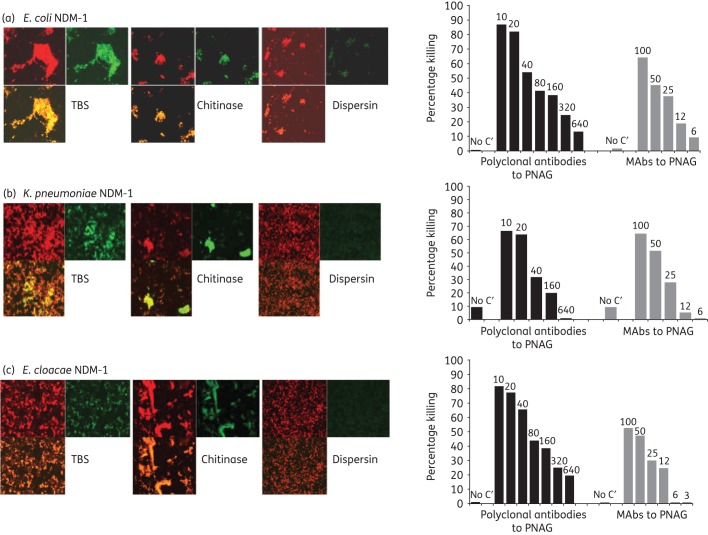
Figure 3.
PNAG production by NDM-1-producing Enterobacteriaceae and in vitro killing by PNAG antibodies. Detection of PNAG on the surface of NDM-1-producing Enterobacteriaceae strains using immunofluorescence confocal microscopy (left panels). Binding of MAb F598 to PNAG conjugated to AF488 results in green fluorescence. SYTO 83 was used to visualize DNA (red fluorescence). Bacteria tested: NDM-1-producing E. coli, K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae (a, b, c left panels, respectively). Digestion with the PNAG-degrading enzyme dispersin B, but not a control enzyme, chitinase, resulted in loss of binding of MAb F598. Opsonophagocytic killing of NDM-1-producing E. coli, K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae (a, b, c, right panels, respectively) mediated by polyclonal antibodies or MAbs to PNAG. Bars represent mean percentage of killing relative to control containing NGS or the control MAb F429. All standard deviations (not shown) were <15%. Assays were done in duplicate. C′, complement; absence of killing arbitrarily assigned as 1% killing. Dilutions of polyclonal antibodies and concentrations (in μg) of MAbs to PNAG tested are provided at the top of each bar.