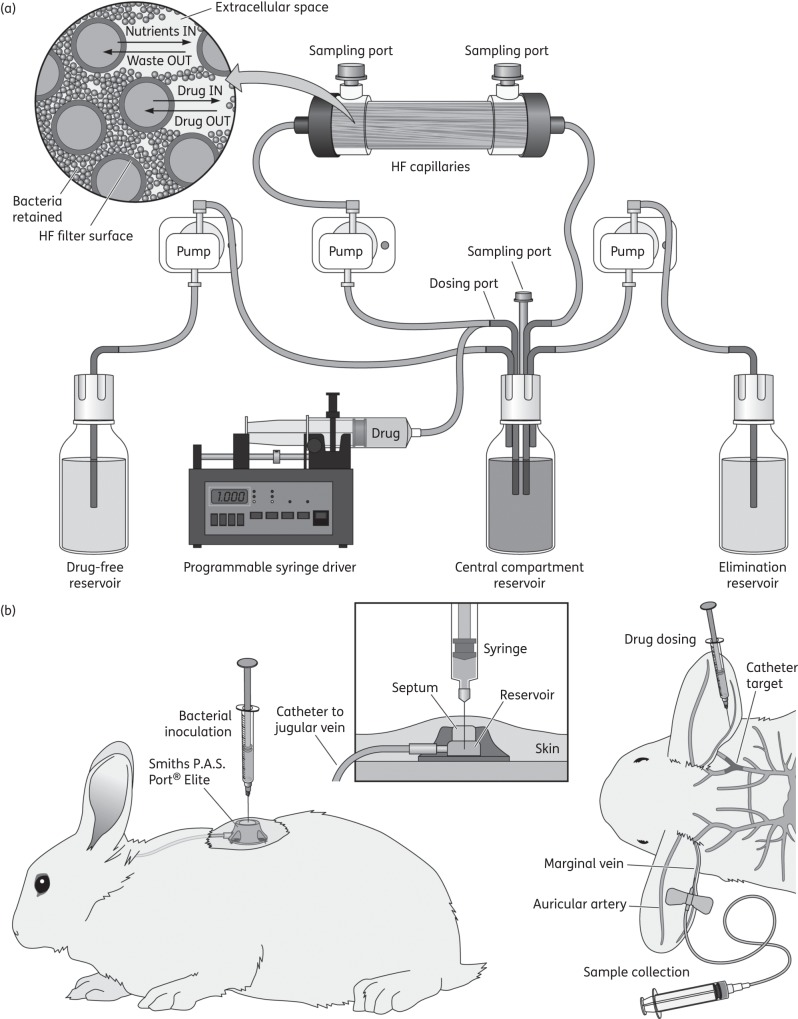
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of neonatal CLABSI models. (a) In vitro, HFIM: MH broth was pumped from a central compartment through an HF cartridge (FiberCell Systems, Frederick, MD, USA). Vancomycin was injected into the central compartment using a programmable syringe driver (Aladdin pump, World Precision Instruments, UK). Two peristaltic pumps (205U, Watson-Marlow, UK) were used. Fresh medium was pumped from a reservoir into the central compartment and the same volume removed as waste. The first pump had a speed rate that represented the neonatal simulated vancomycin elimination t1/2. (b) In vivo, rabbit model: central venous access was established with a rabbit jugular vein catheter with a Smiths P.A.S. Port® Elite (SAI Infusion Technologies, IL, USA) under general anaesthesia, to enable CoNS infection through the central line and biofilm formation.