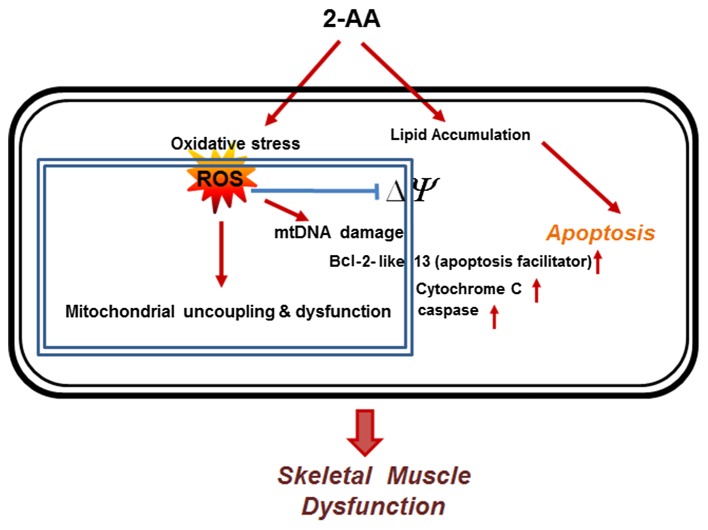
Figure 5.
Representative schematic diagram showing that 2-aminoacetophenone (2-AA) induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in skeletal muscle. 2-AA induces oxidative stress by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS). The oxidative damage and ROS reduce mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨ), and release Bcl-2 and cytochrome c, which promotes apoptosis. Lipid accumulation following 2-AA treatment potentially generates apoptotic signals in the cells (58,59). The red arrows denote the induction of the cellular components.