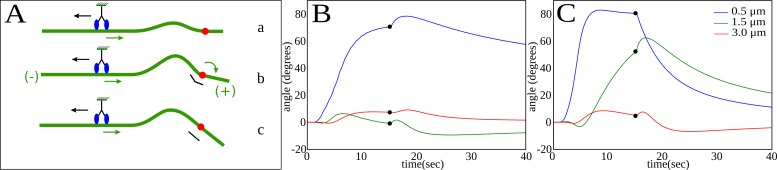
Fig 4. Effect of overhanging segment length on the rotation of the tip.
(A) The sketch shows how a local increase in curvature during bend formation drives tip rotation. A local bend (a) generates a bending moment across the pinning point (b). Motion of the overhanging segment is opposed by friction, but given enough time, the tip rotates to straighten the segment (c). (B) Orientation of a growing microtubule tip as a function of time. The microtubule is initially pinned at different distances from the tip: 0.5 micron (blue), 1.5 micron (green) and 2.5 micron (red) and unpinned after 15 seconds (black dot). (C) Orientation of a non-polymerizing microtubule tip as a function of time. The microtubule is initially pinned at different distances from the tip: 0.5 micron (blue), 1.5 micron (green) and 2.5 micron (red) and unpinned after 15 seconds (black dot).