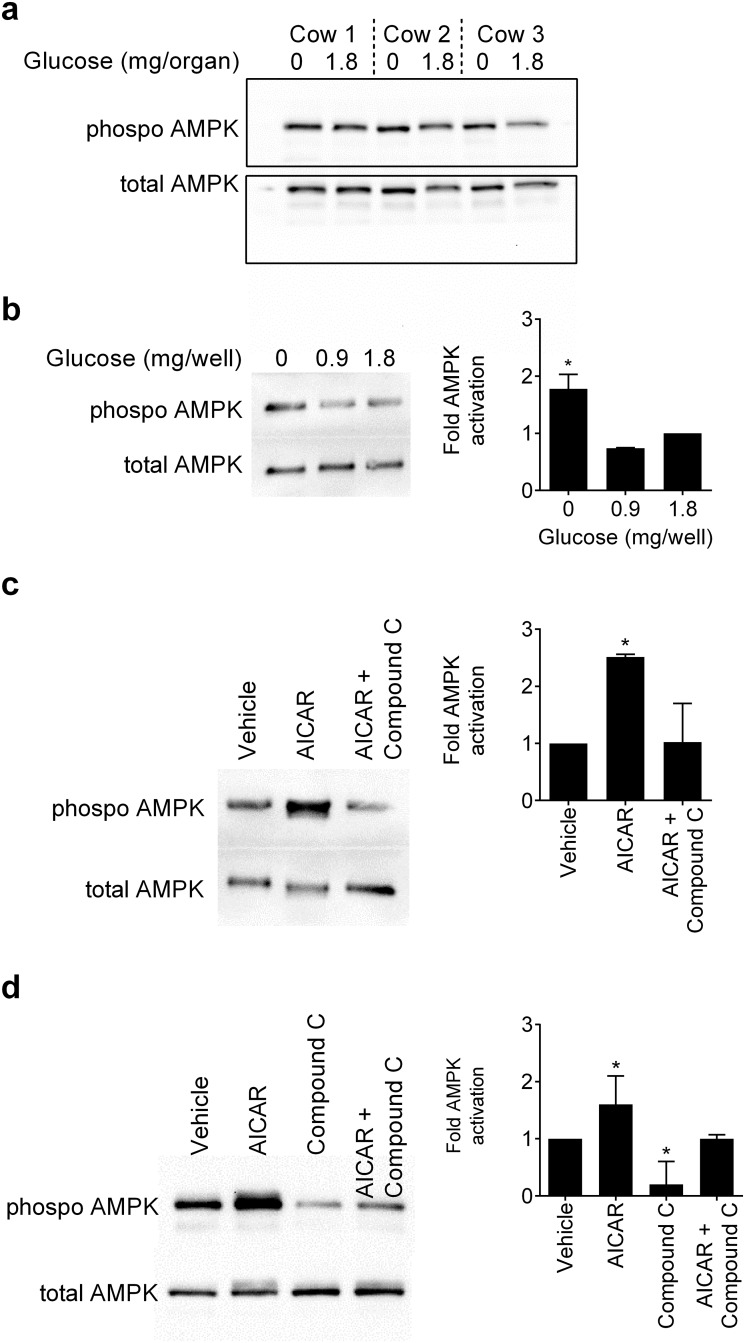
Fig 3. Expression of phosphorylated AMPK.
(a) An image of a Western blot from 3 animals where ex vivo organ cultures of endometrium were cultured for 4 h in medium containing 0 or 1.8 mg/organ glucose, the samples homogenized and Western blotting performed to evaluate phosphorylated AMPK, with total AMPK used as a loading control. (b) Endometrial stromal cells were cultured for 4 h in medium with 0, 0.9 or 1.8 mg/well glucose, or (c) cultured for 2 h in medium with vehicle, 1 mM AICAR, or AICAR with 50 μM Compound C. (d) Epithelial cells were cultured for 2 h in medium with vehicle, 1 mM AICAR, 50 μM Compound C, or AICAR with Compound C. (b-d) The cells were collected and immunoblotted for phosphorylated AMPK, with protein loading evaluated and normalised to expression of total AMPK. The left panel shows a representative blot from three independent experiments and the right panel mean + SEM of densitometric analysis of phosphorylated AMPK normalized to total AMPK protein, expressed as fold activation of 1.8 mg/organ glucose (b) or vehicle (c, d), and analyzed by Mann-Whitney U test, * P < 0.05.